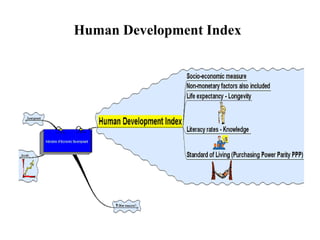
The document discusses perspectives on health and development. It begins by outlining the objectives of the session which are to discuss views of health, explain poverty, concepts of development, and indicators of economic development. It then explores factors that affect health like poverty, education, nutrition, and sanitation. Poverty is defined and its main causes like unemployment and low social protections are outlined. Strategies for poverty reduction like fair wealth distribution and increasing public revenues are presented. Different perspectives on health as a right, consumption good, and investment are introduced. Development is defined as social, economic, and institutional processes that improve life. Objectives and characteristics of development are defined. Finally, indicators of economic development like GNP, GDP, and the