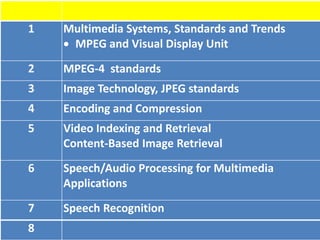
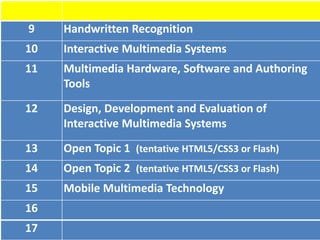
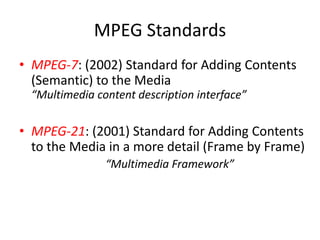
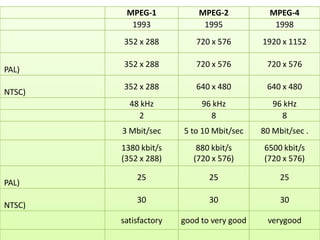
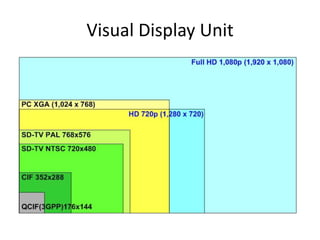
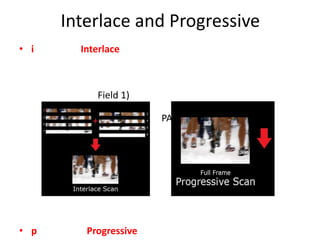
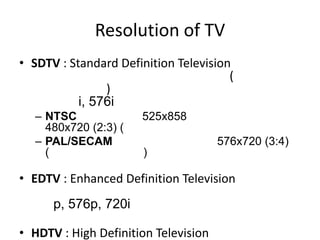
This document discusses multimedia technology and standards. It provides an overview of topics covered in the MIT 628 course, including MPEG standards, image and video compression, multimedia hardware and software, and mobile multimedia. Key standards discussed are MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4, and HDTV resolutions and technologies.