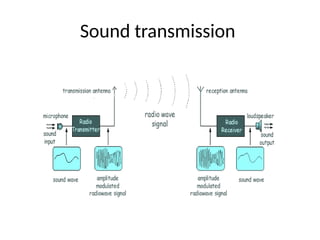
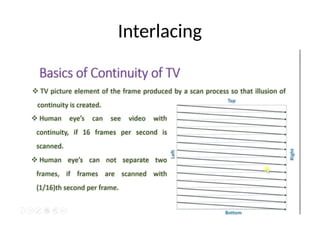
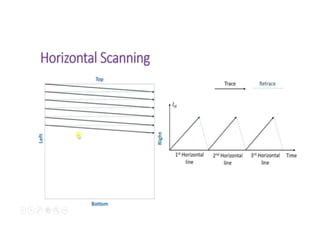
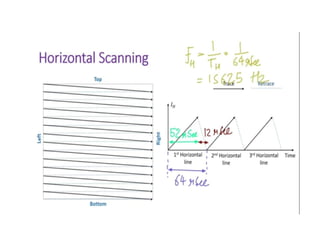
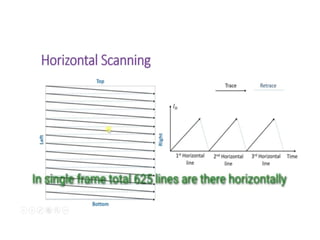
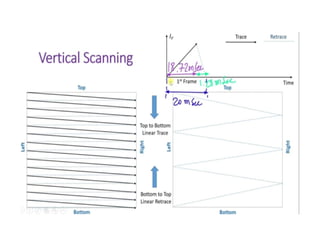
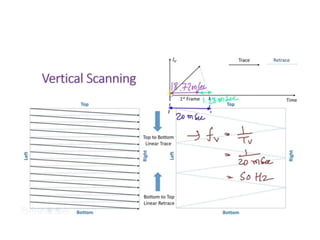
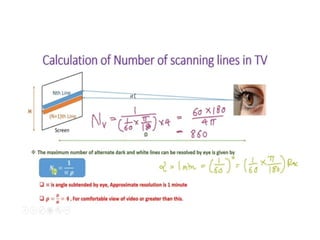
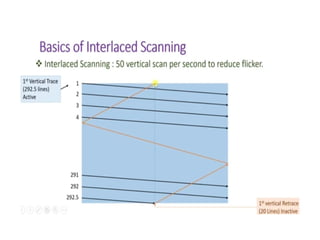
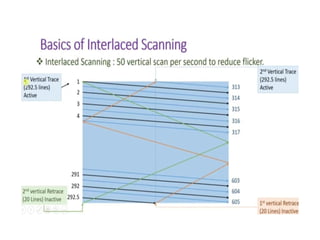
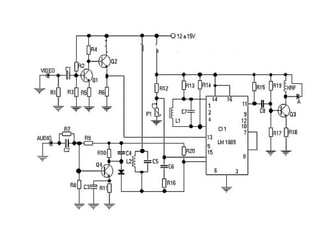
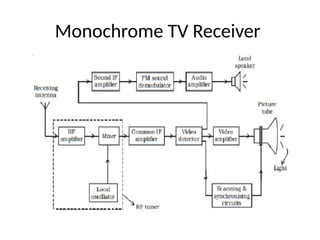
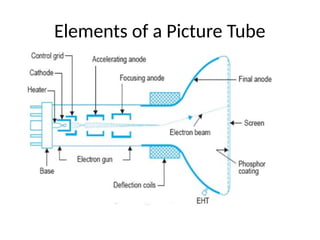
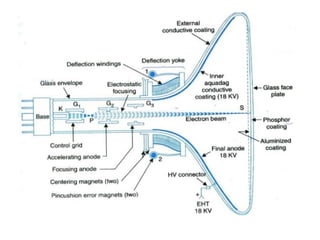
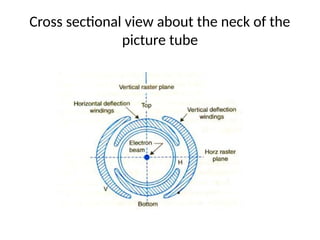
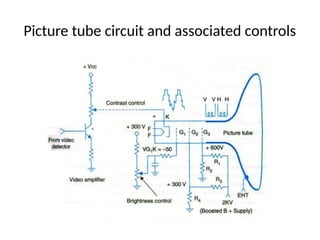
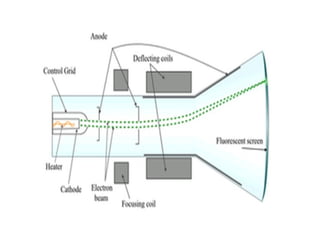
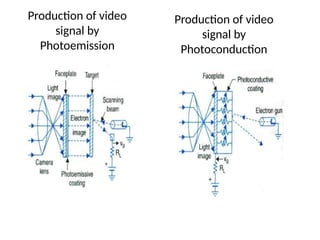
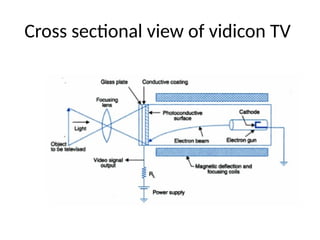
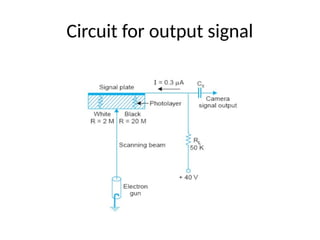
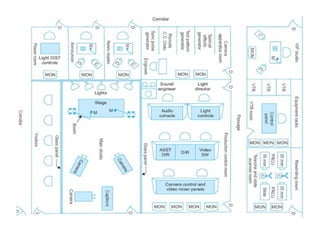
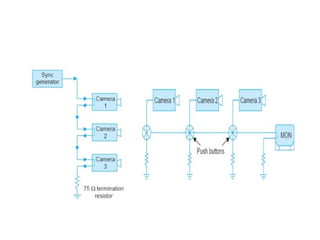
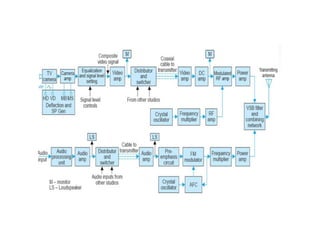
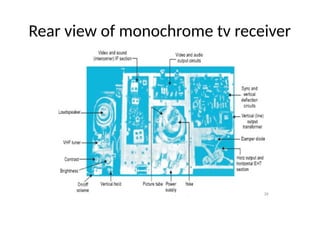
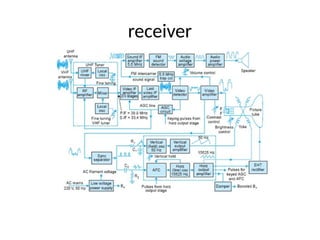
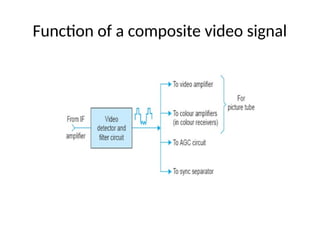
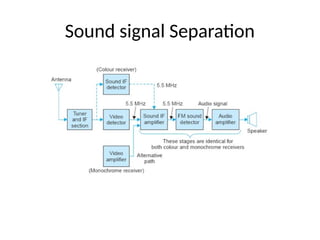
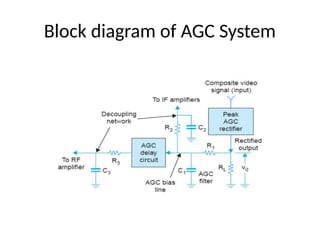
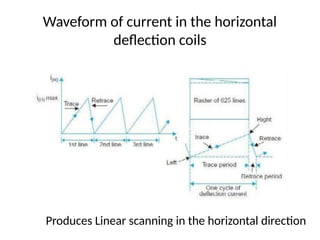
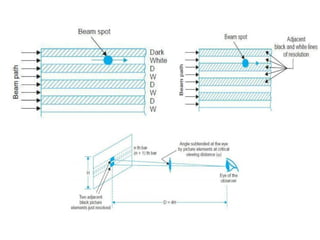
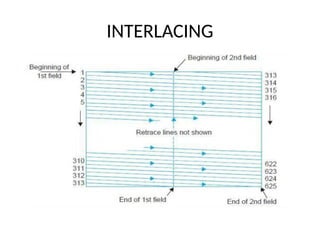
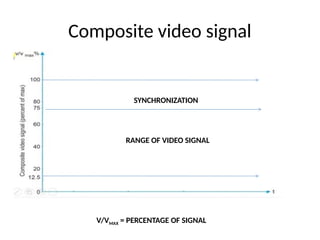
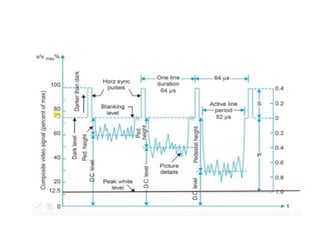
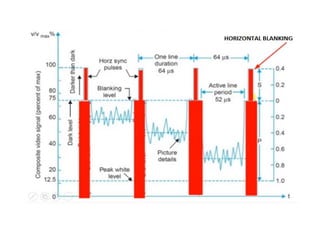
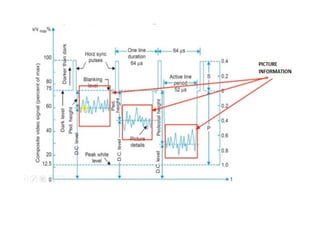
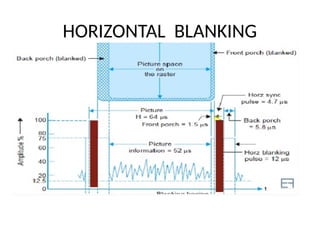
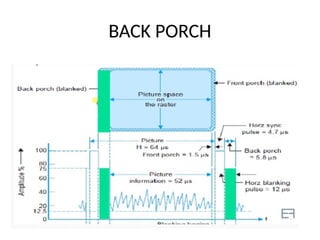
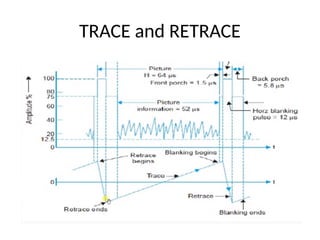
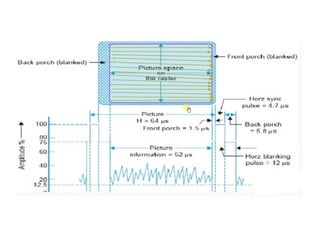
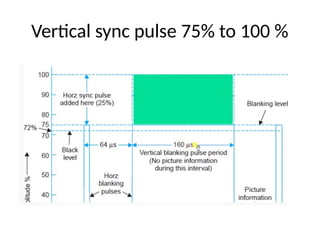
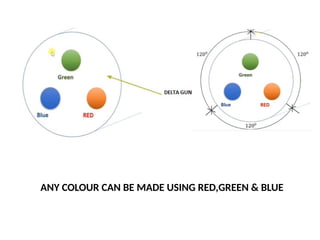
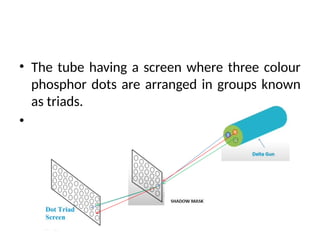
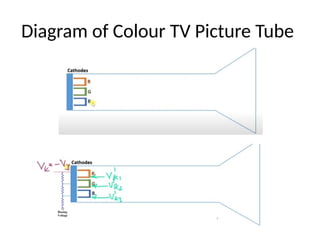
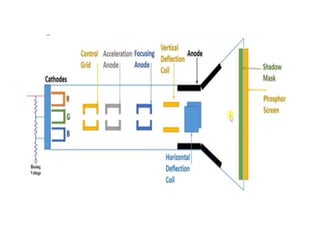
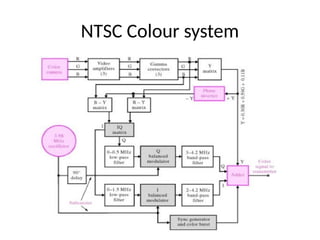
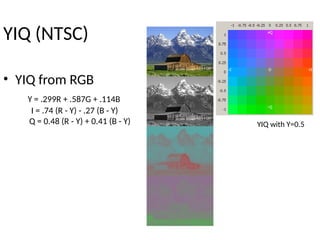
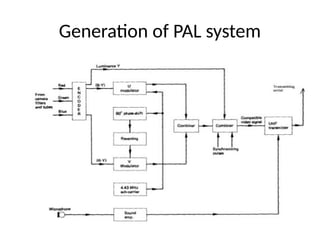
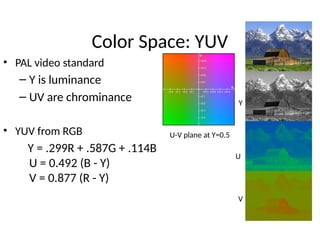
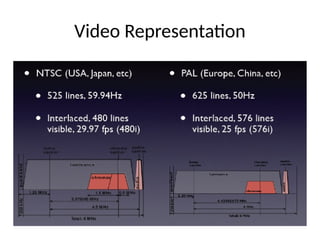
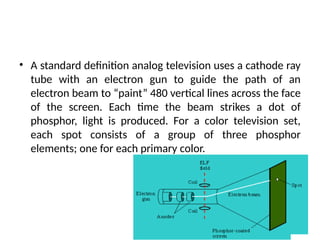
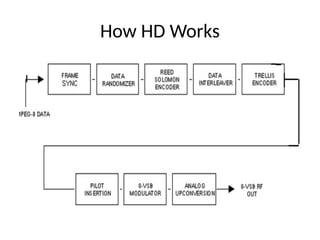
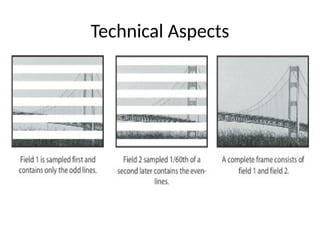
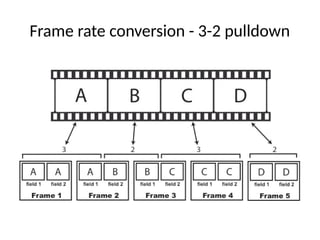
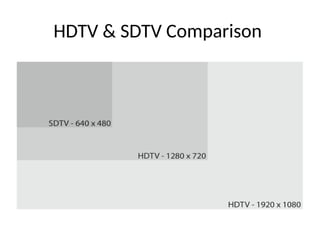
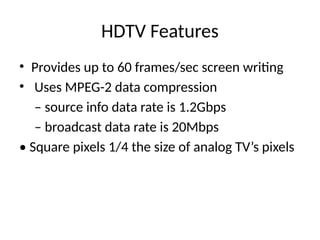
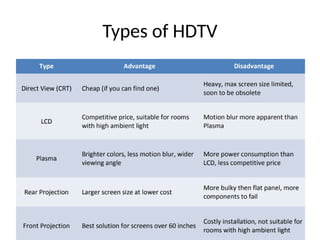
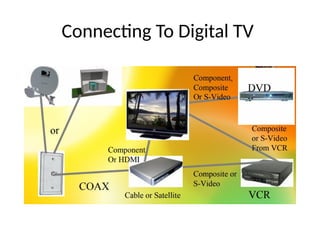
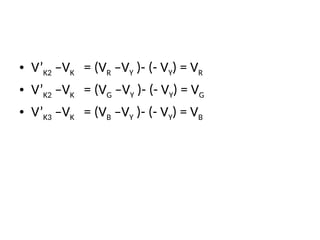The document provides an overview of television standards and systems, including the components and functioning of monochrome and color television, as well as the evolution towards high-definition television (HDTV). It details video signals, synchronization pulses, and the technical aspects of various TV technologies such as DLP, LCD, and plasma displays. The document also discusses different TV standards (NTSC, PAL, SECAM), as well as the historical development and impact of HDTV on broadcasting and consumer technology.