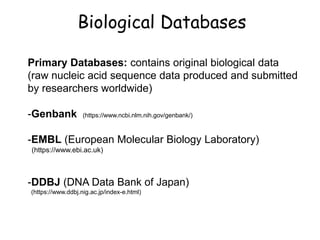
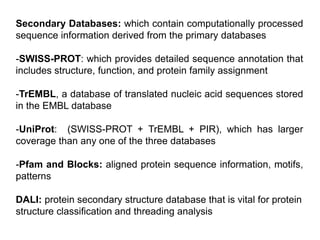
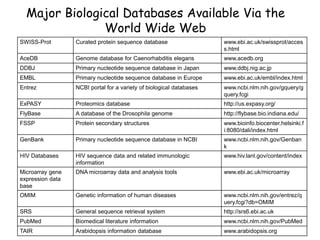
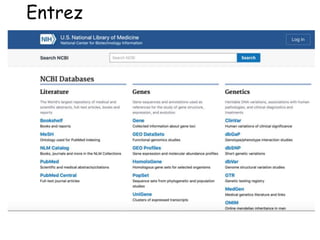
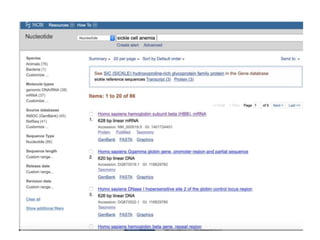
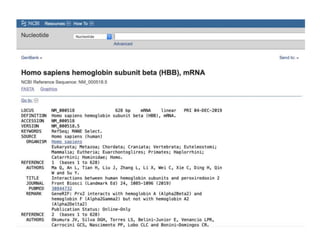
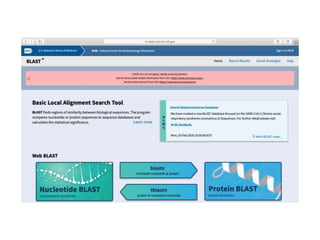
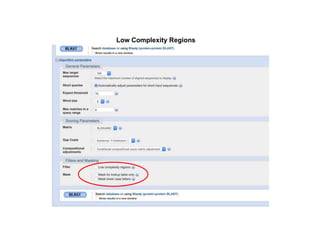
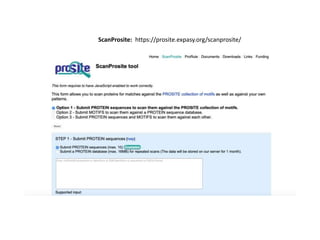
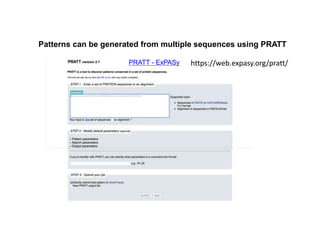
The document discusses various types of biological databases including primary databases that contain original sequence data, secondary databases that contain processed sequence data, and specialized databases. It provides examples of major biological databases available on the web including GenBank, SWISS-PROT, and Pfam. It also discusses algorithms and tools for sequence analysis like BLAST and patterns searches with PROSITE and MEME.









![PHI-BLAST
PROSITE pattern for the kinase active site, starting from the conserved DRH and
making use of the very conserved DFG region: D-R-H-[NS]-[DS]-N-[IL]-x-[IV]-x-[DEK]-
[DGST]-G-[NQR]-L-F-H-I-D-F-G
The above query sequence and the PROSITE pattern used as inputs for the PHI-
BLAST search (see next slide)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/handsontraining08022023-230413032908-297e7d24/85/Hands-on-training_biological_databases-ppt-23-320.jpg)
