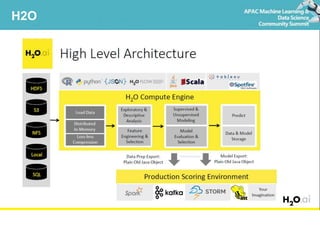
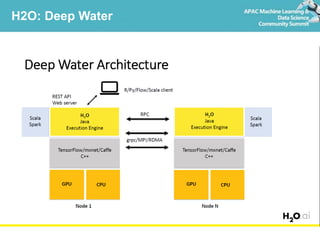
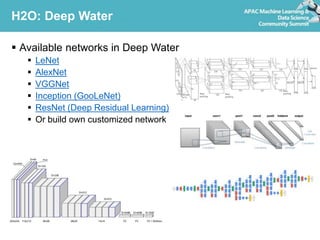
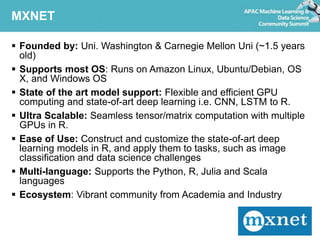
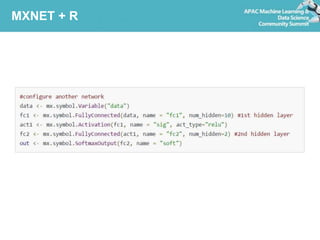
Deep learning refers to artificial neural networks with many layers. This document provides an introduction to deep learning and neural networks, including their strengths and weaknesses. It discusses popular deep learning libraries for R like H2O and MXNet. H2O allows users to perform distributed deep learning on large datasets using R. MXNet provides state-of-the-art deep learning models and efficient GPU computing capabilities for R. The document demonstrates how to customize neural networks and run deep learning models with H2O and MXNet in R.