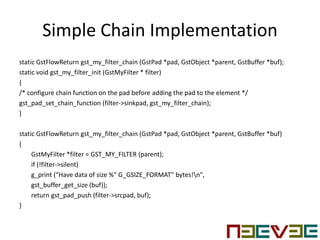
Gstreamer plugin development involves creating elements, plugins, and pads. Elements are the core components that process media streams. Plugins contain implementations of elements and are loaded on demand. Pads negotiate media flow between elements and ensure type compatibility. The chain function processes incoming buffers and passes them downstream. A simple pass-through filter would implement chain to push incoming buffers to the output pad without modification.

















![Element Meta data
gst_element_class_set_static_metadata (klass,
"An example plugin",
"Example/FirstExample",
"Shows the basic structure of a plugin",
"your name <your.name@your.isp>");
static void gst_my_filter_class_init (GstMyFilterClass * klass)
{
GstElementClass *element_class = GST_ELEMENT_CLASS (klass);
[..]
gst_element_class_set_static_metadata (element_klass,
"An example plugin",
"Example/FirstExample",
"Shows the basic structure of a plugin",
"your name <your.name@your.isp>");
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gstreamerplugindevelopmentvii-160430044629/85/Gstreamer-plugin-development-20-320.jpg)