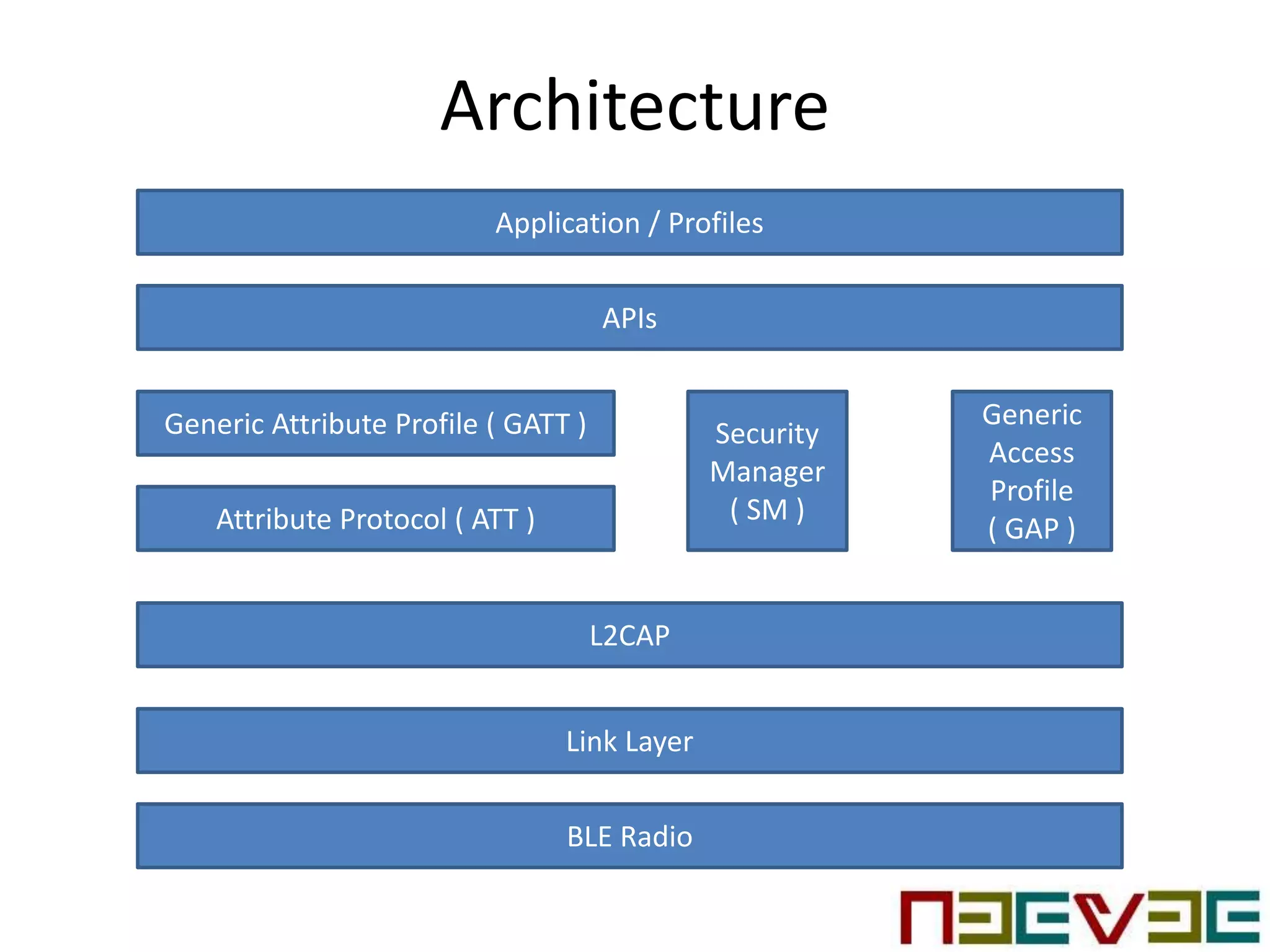
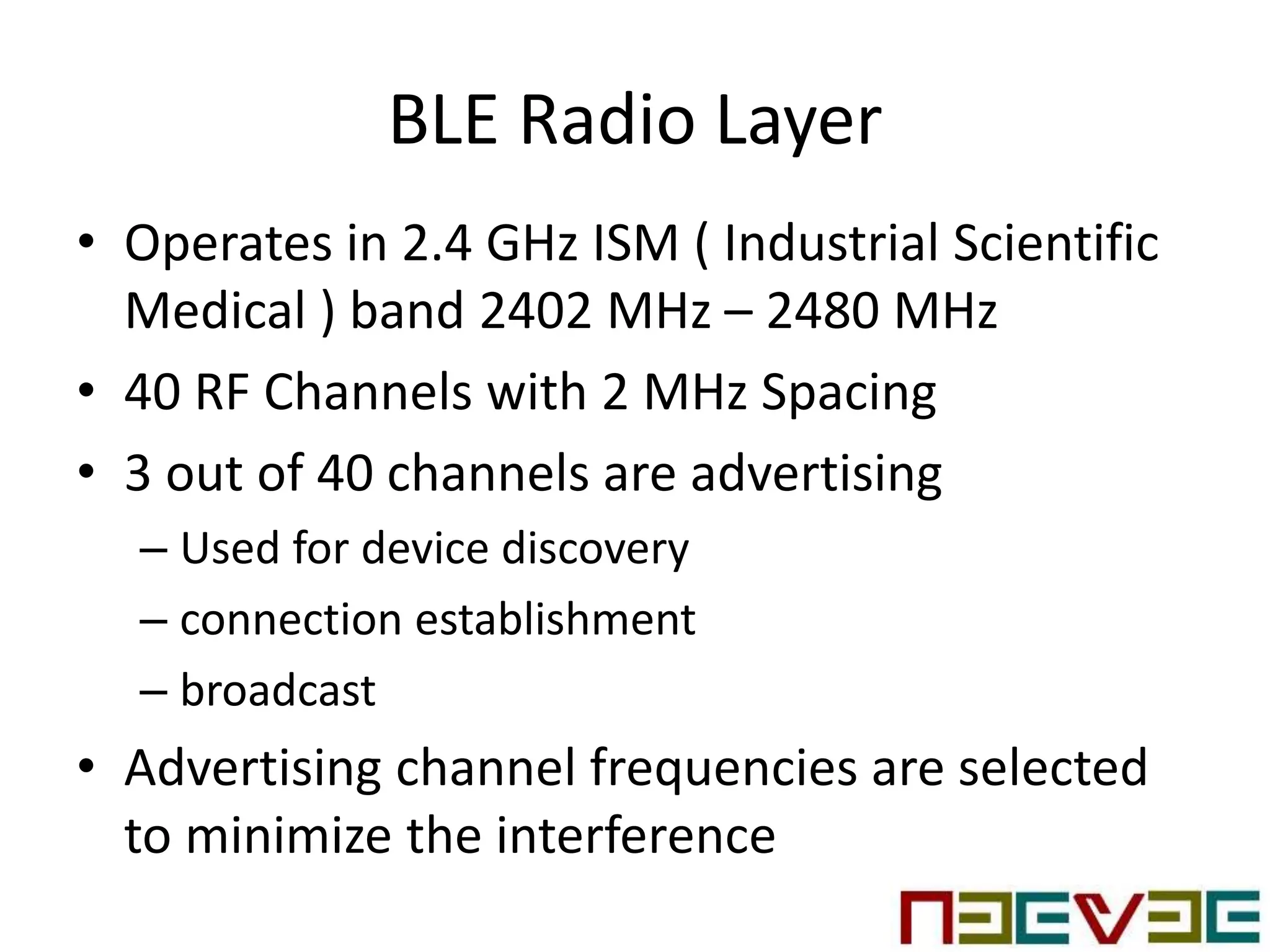
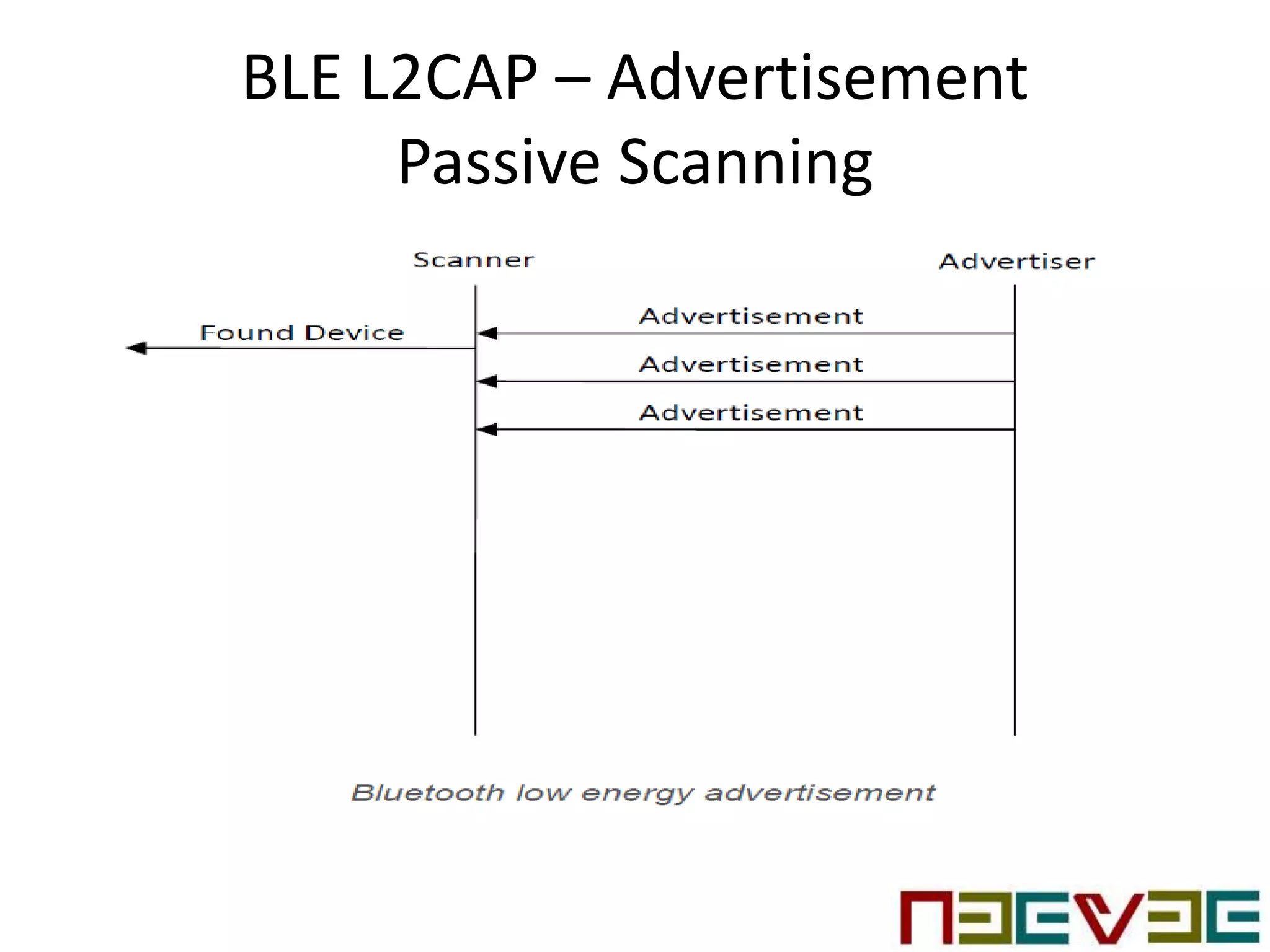
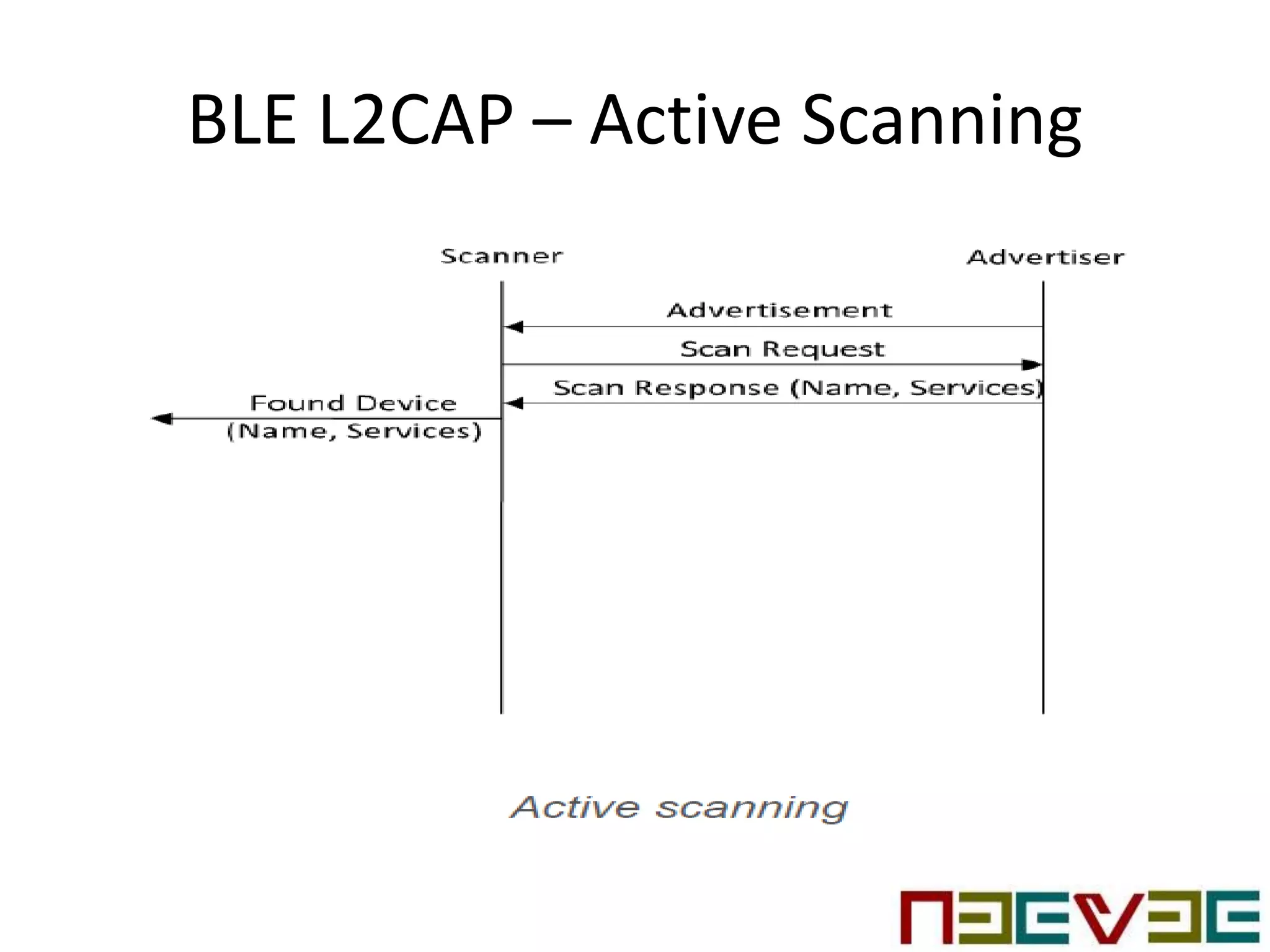
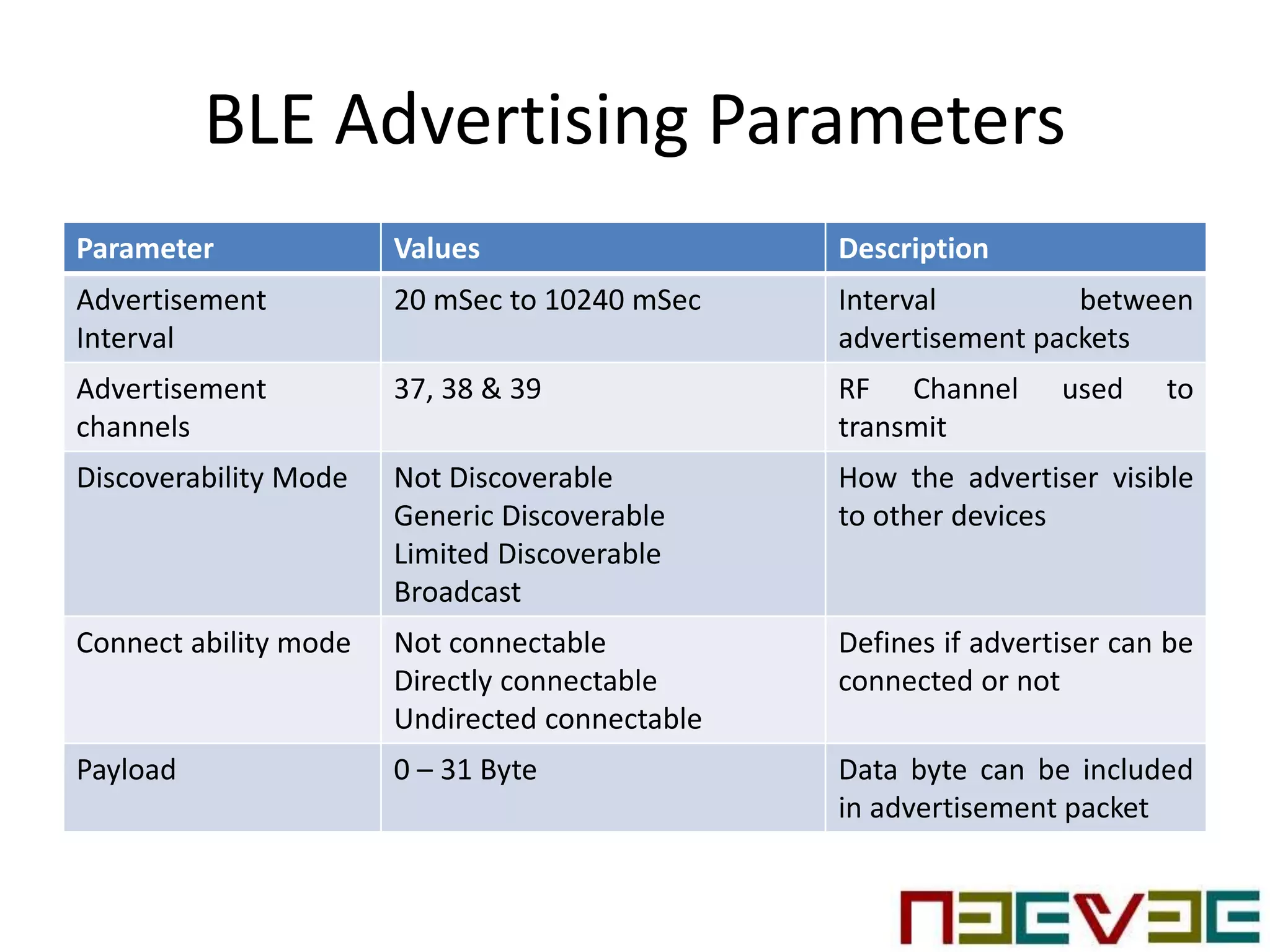
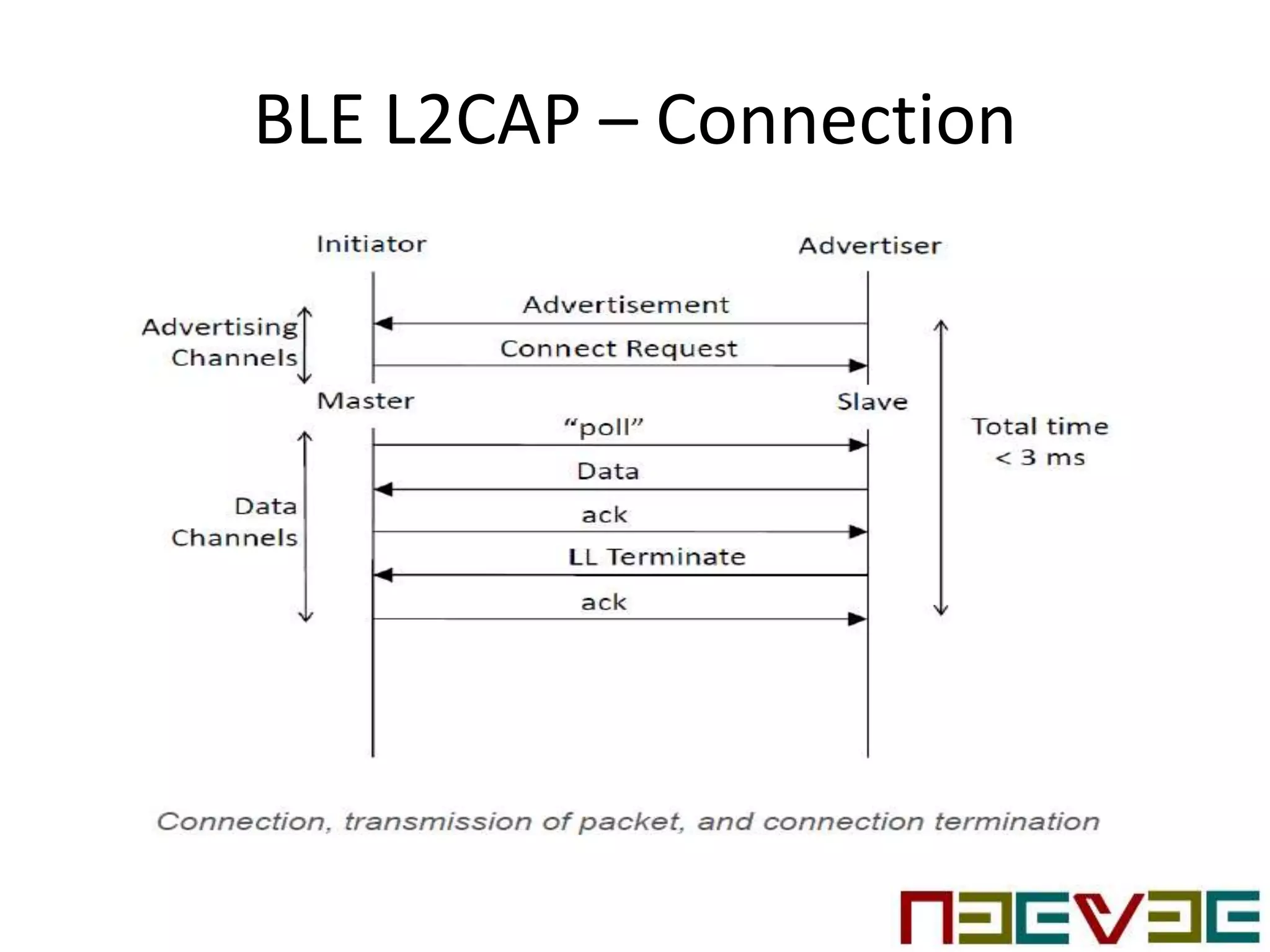
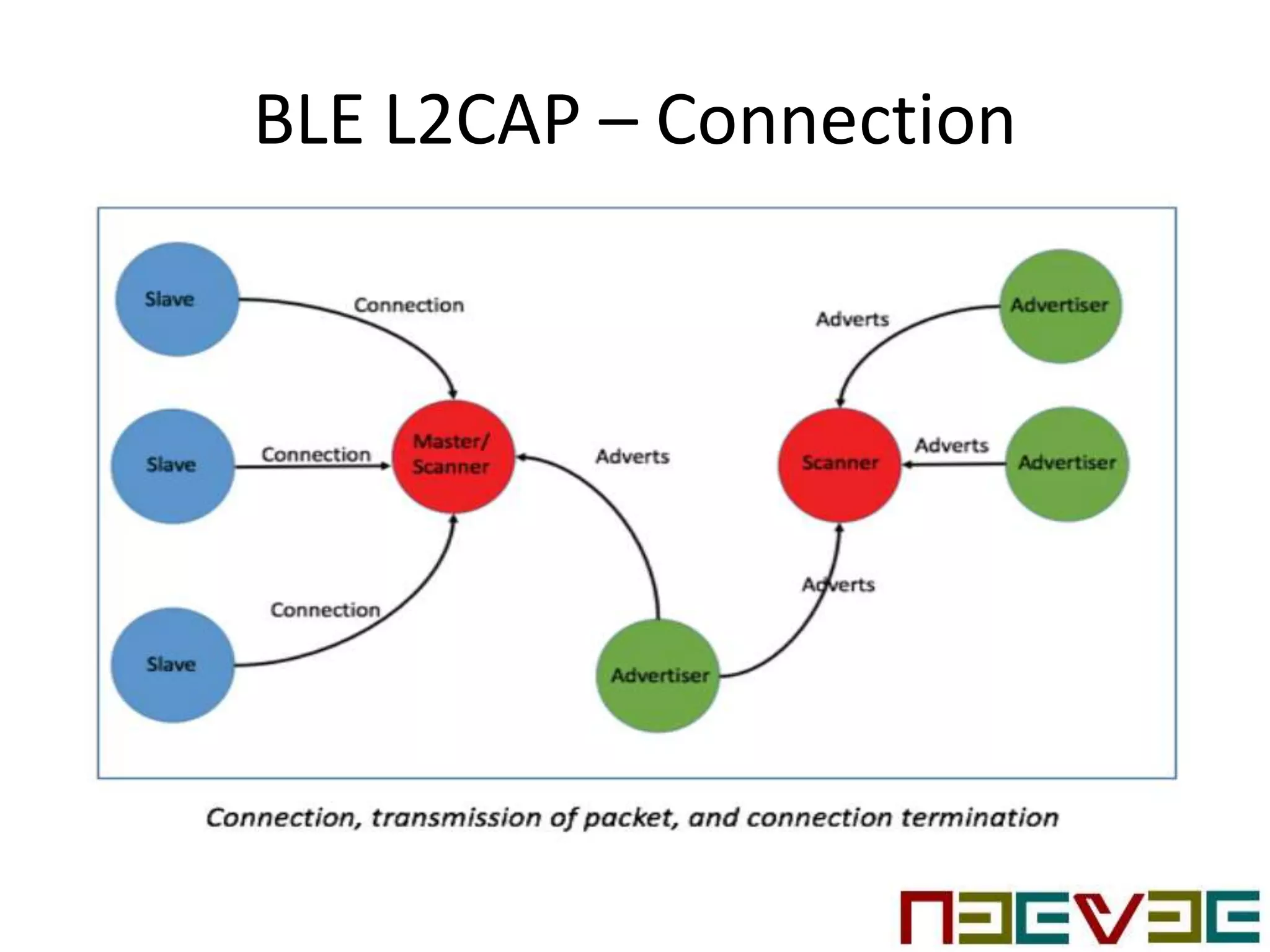
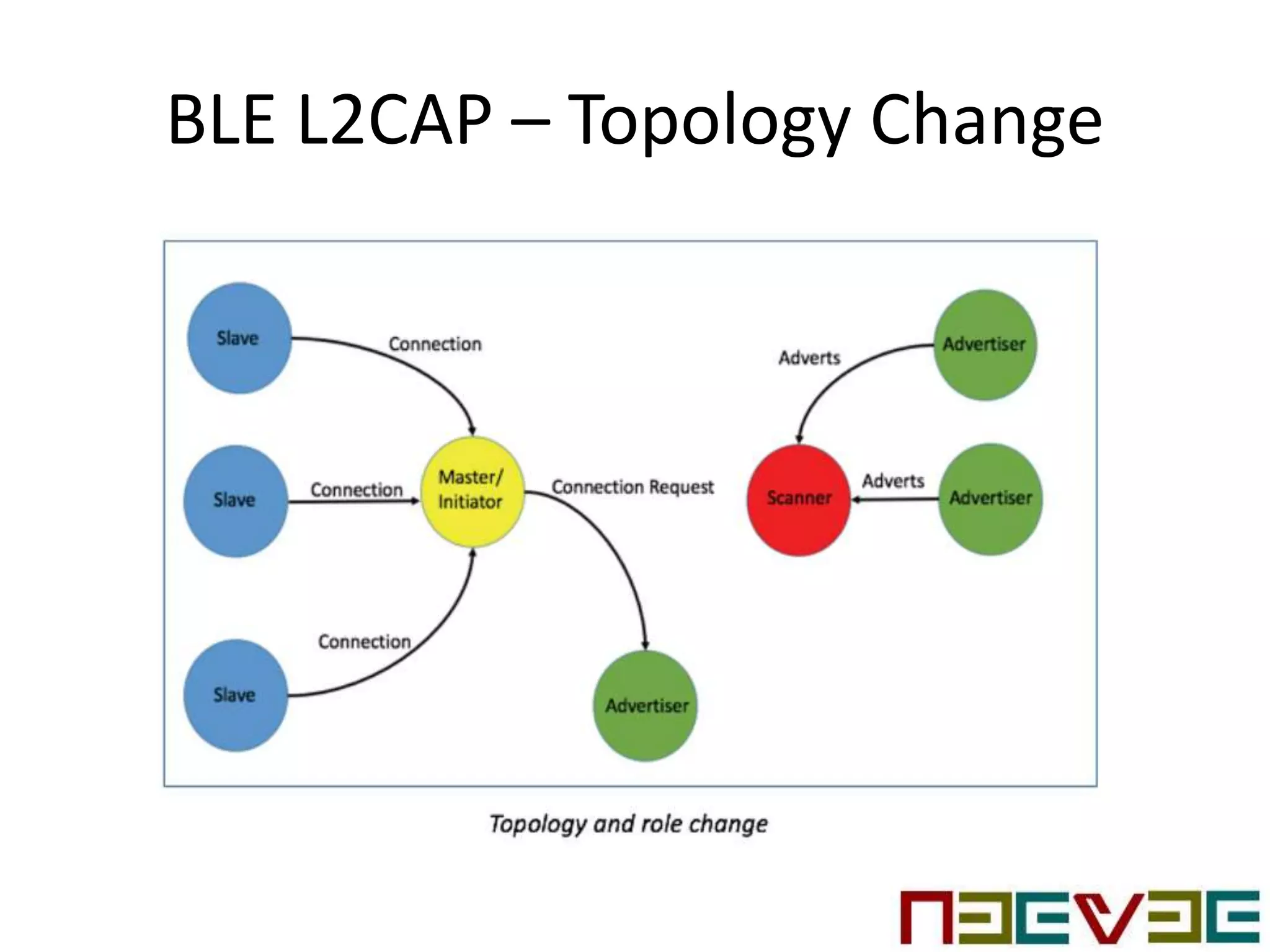
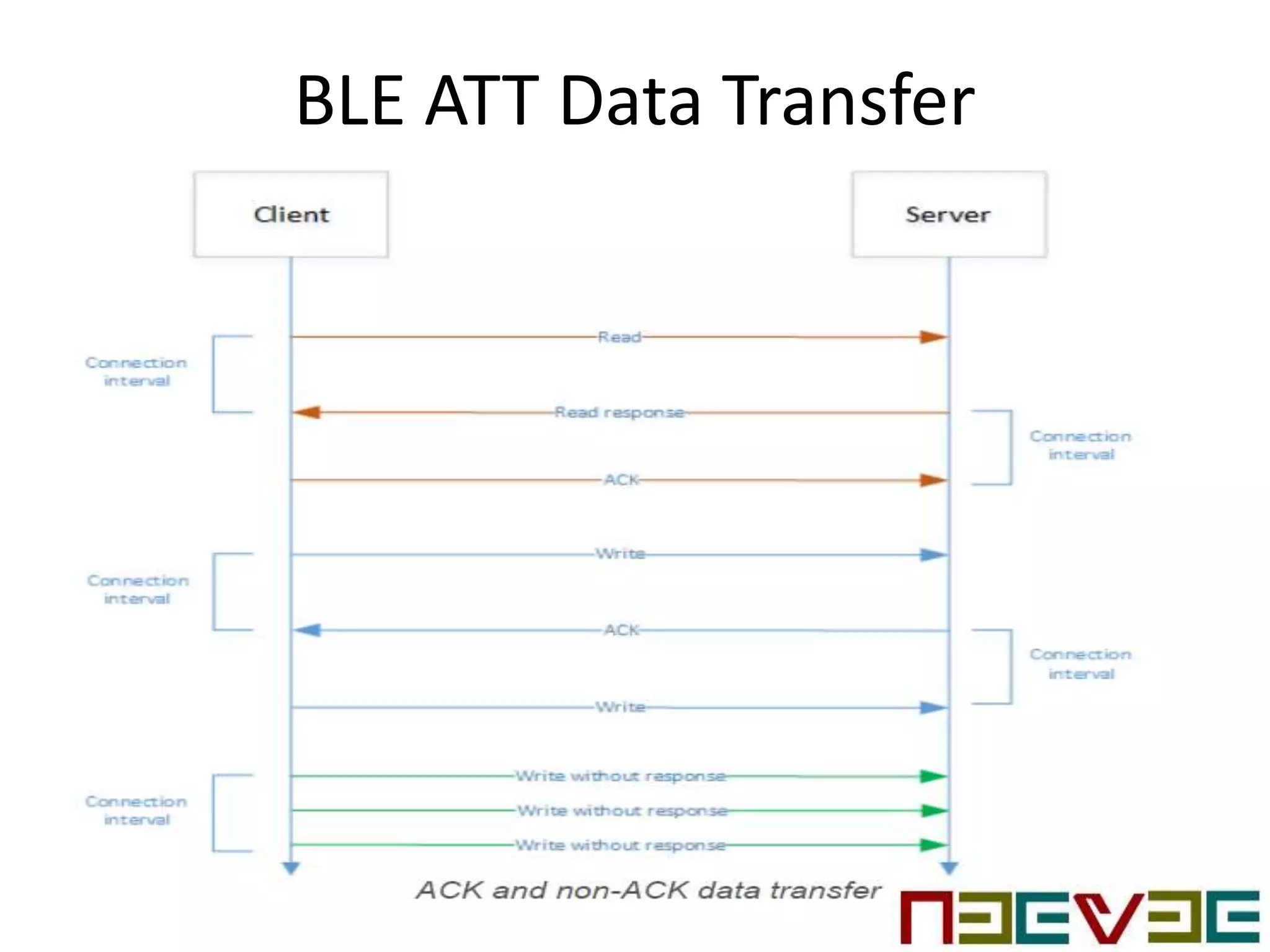
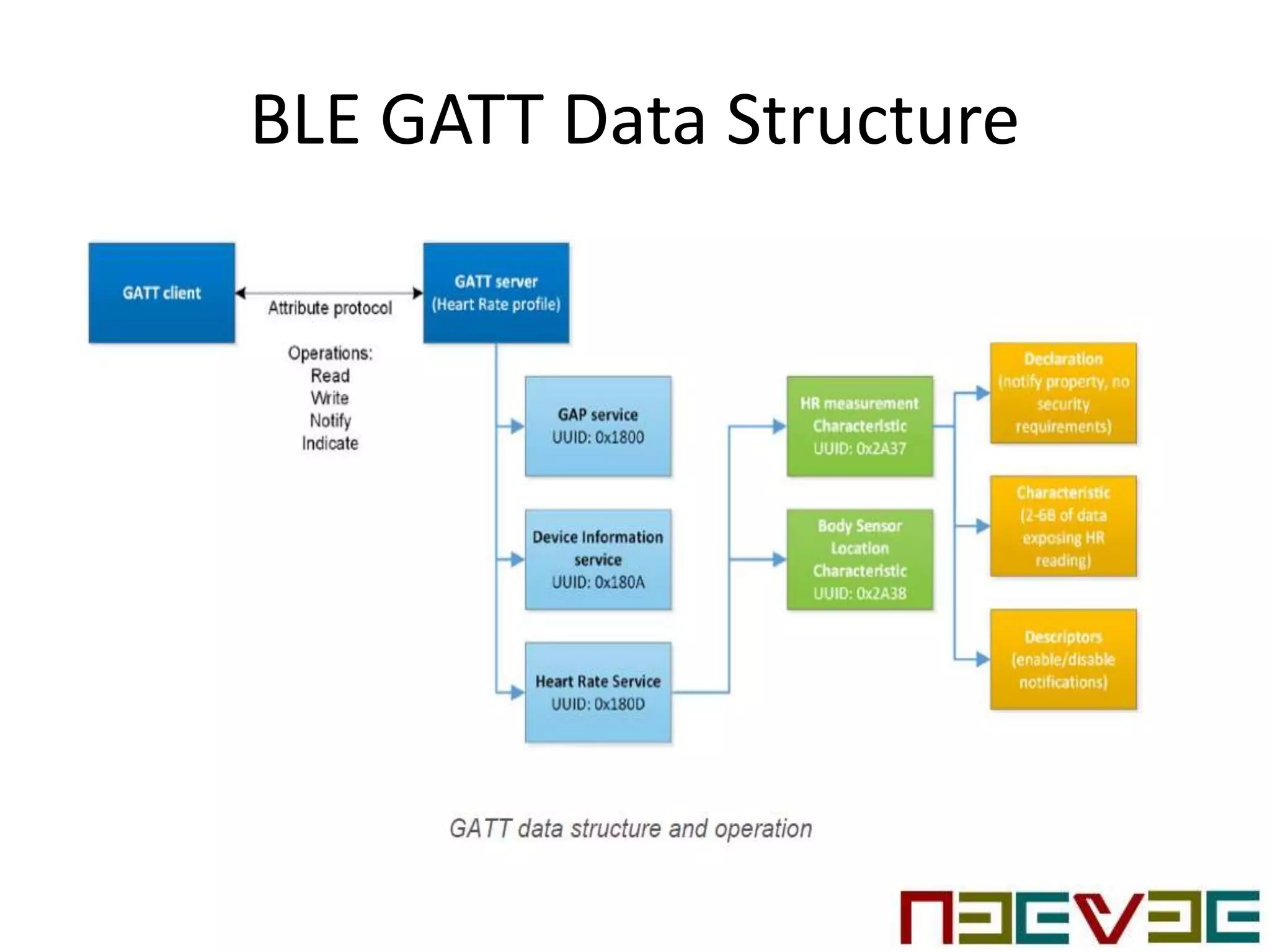
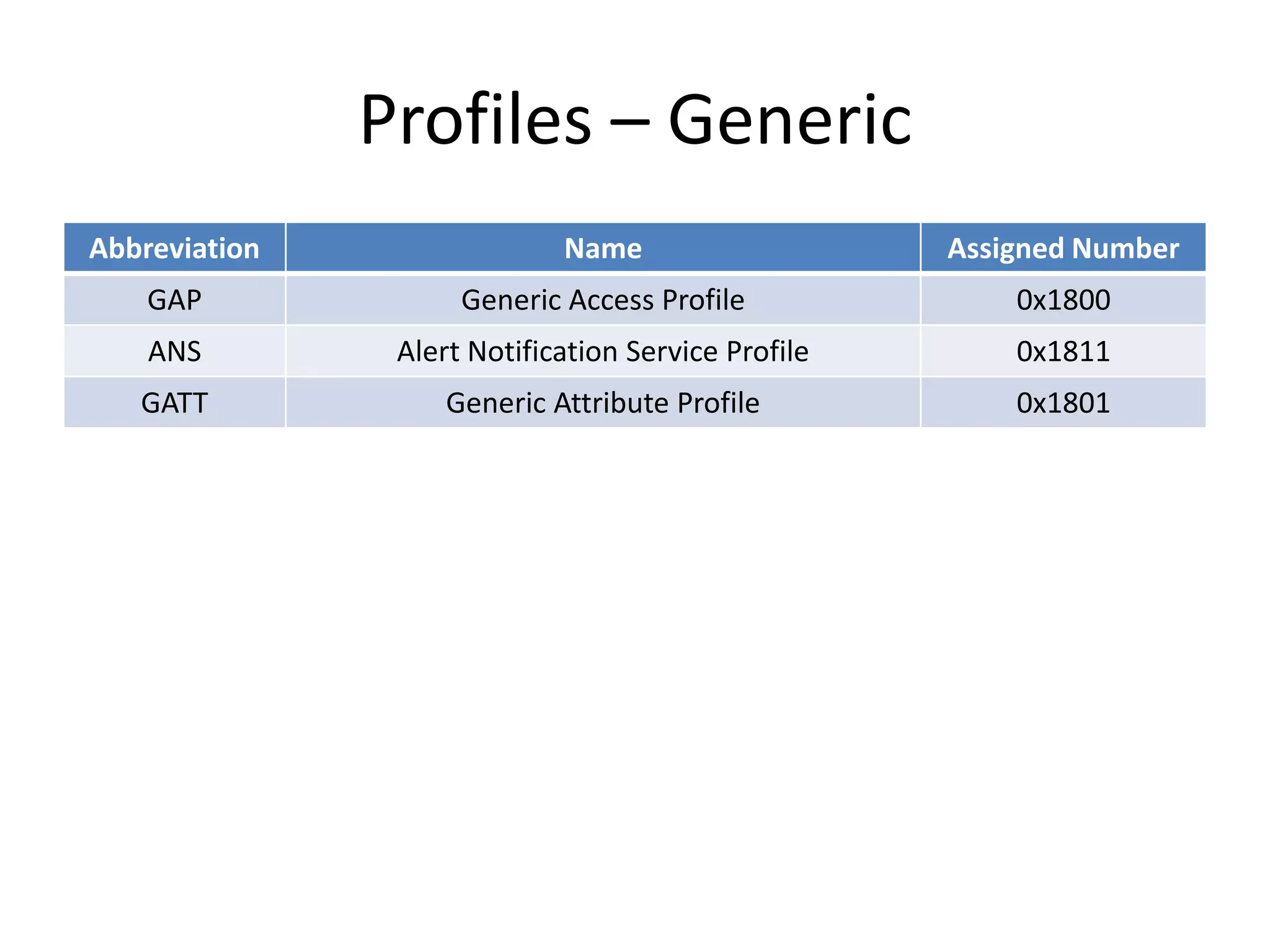
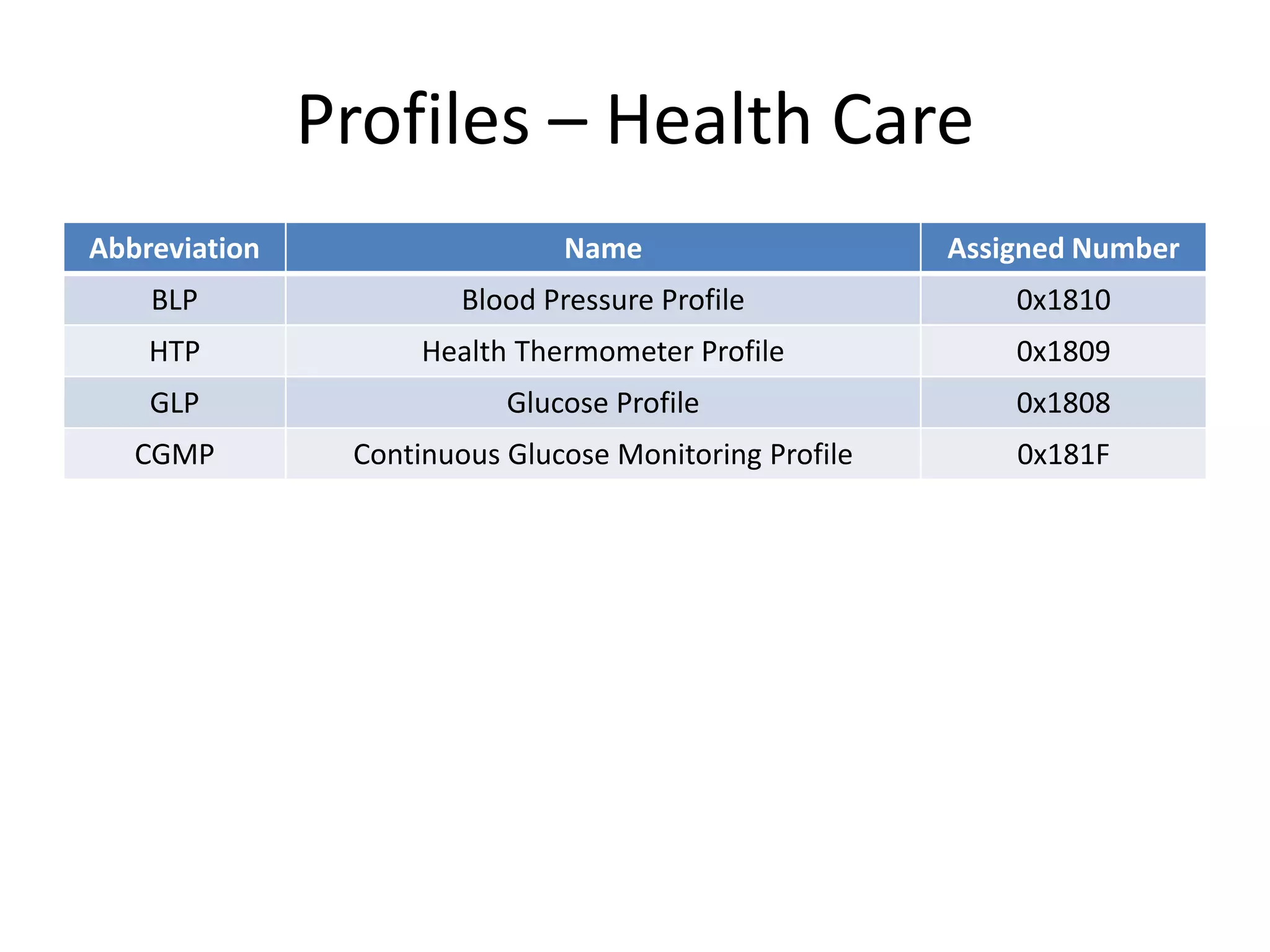
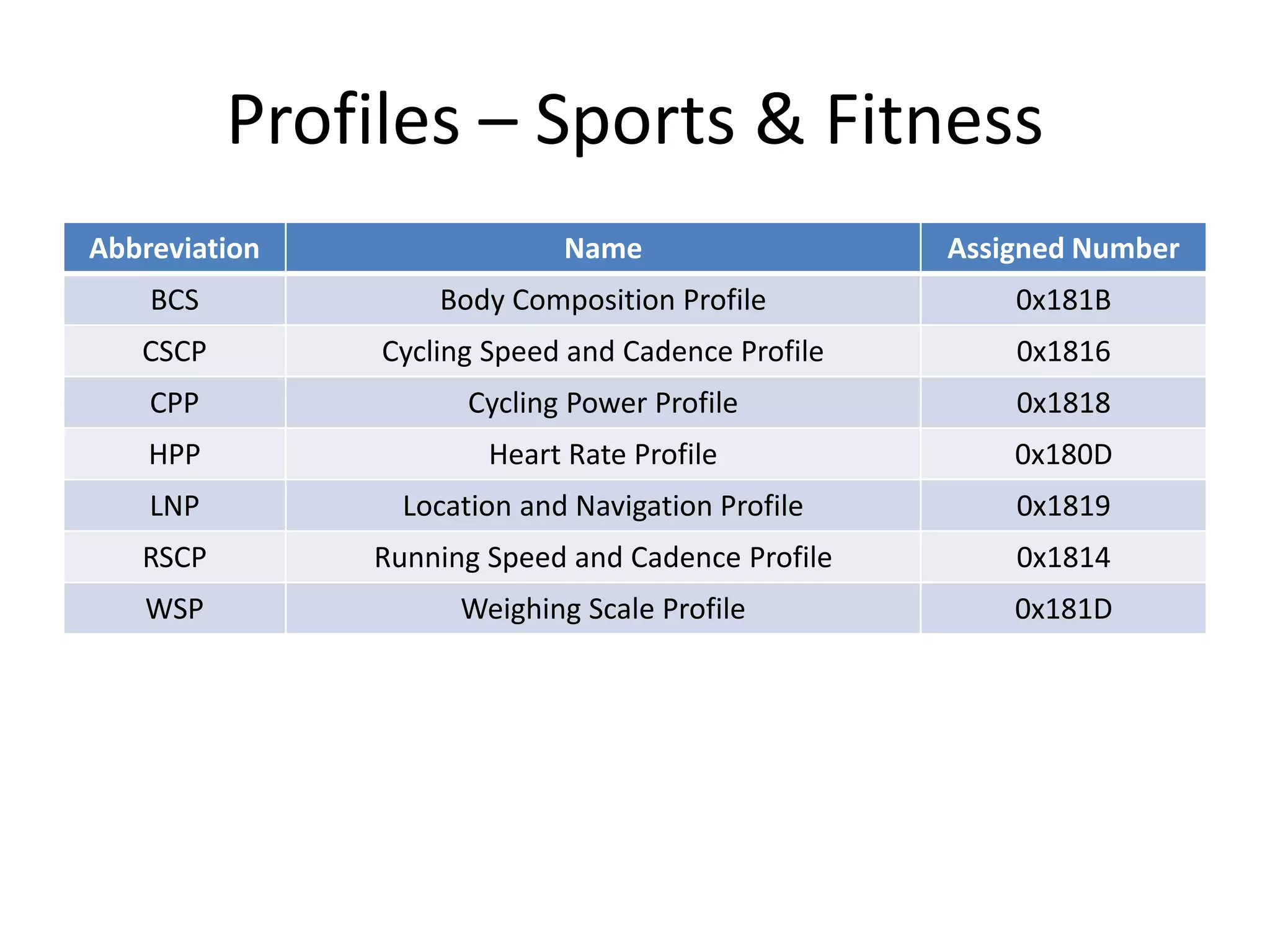
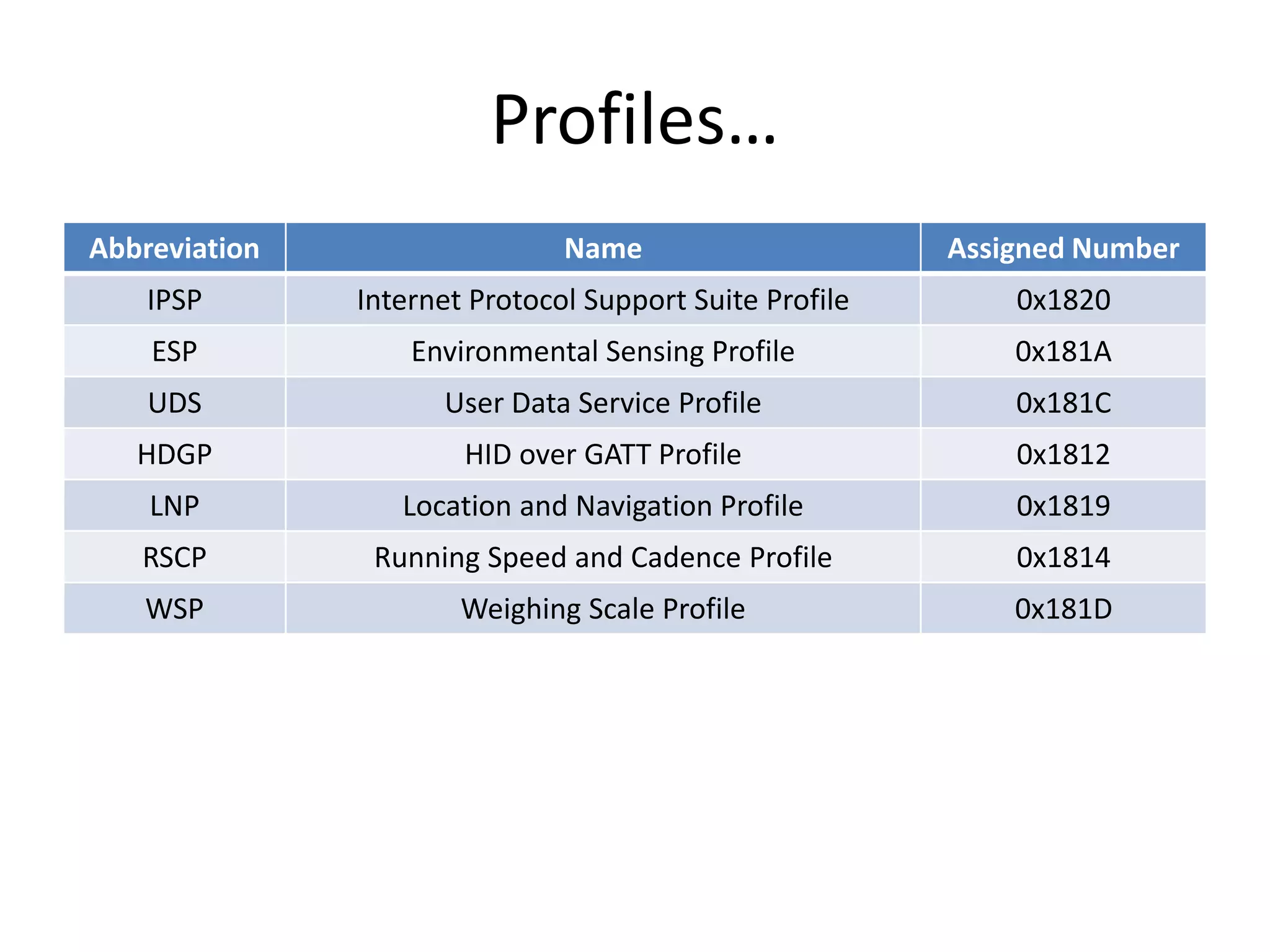
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is a wireless personal area network technology aimed at various applications such as healthcare and fitness, characterized by low power consumption and compatibility with existing devices. It operates in the 2.4 GHz band and utilizes protocols like L2CAP and GATT for data transmission and device communication. BLE features roles such as broadcaster and observer, supports security measures like encryption and pairing, and includes various profiles for specific applications.