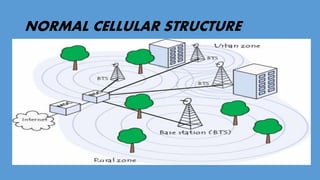
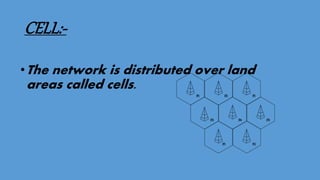
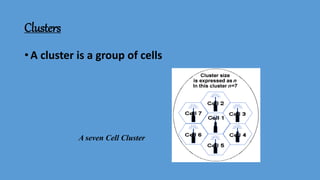
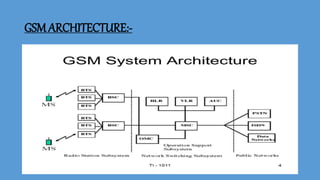
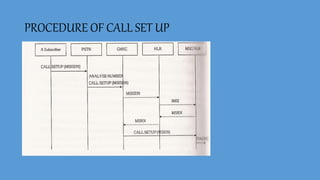
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication) is a 2G digital cellular network. It was developed to address fragmentation issues in first-generation analog cellular systems and introduce digital technology and networking architectures. GSM specifies services, architecture, and frequencies. It uses a SIM card for user identification and supports voice calls and data services. GSM networks are organized into cells managed by switching centers. As users move between cells, the network performs handovers to maintain connections. GSM was followed by 2.5G, 3G, and 4G networks with increasing data speeds and capabilities.