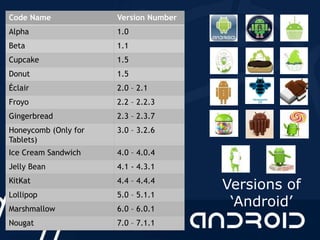
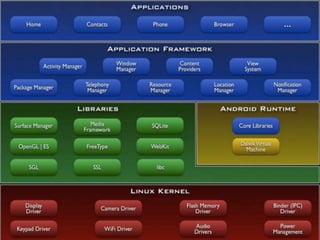
The document provides an overview of Android application development. It defines Android as an open-source, Linux-based operating system for mobile devices. It discusses the history and founding of Android by Andy Rubin in 2003 and its later acquisition by Google in 2005. It also describes the Open Handset Alliance consortium led by Google to develop open standards for mobile devices. The document outlines the major versions of Android and provides details on the Android architecture including its layers - applications, framework, runtime, libraries and the Linux kernel. It introduces Android Studio as the IDE for developing Android apps and describes key app components like activities, intents, services and content providers.