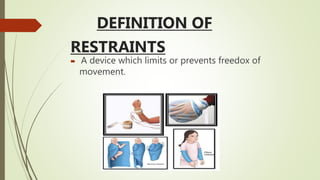
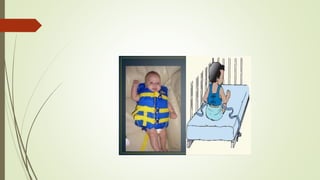
This document discusses different types of restraints used for infants and children in medical settings. It defines restraints as devices that limit freedom of movement. Common purposes of restraints include immobilizing children during procedures to prevent injury and ensure safety. The main types of restraints discussed are mummy restraints, jacket restraints, elbow restraints, extremity restraints, and mittens. Each type is described along with its purpose and application procedure. Potential side effects are also outlined. Proper nursing management of restraints is emphasized, including frequent checks, explanation to families, stimulation of children, and changing positions periodically.






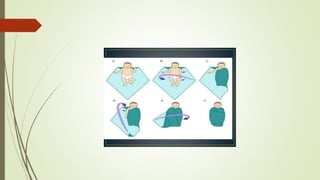
![TYPES OF RESTRAINTS
1. Mummy restraints and modified mummy restraints.
[swaddle]
2. jacket restraints.
3. Elbow restraints.
4. Extremity restraints [ clove hitch restraints ]
5. Mittens.
6. Abdominal binders or restraints.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation12-191209130450/85/Child-restraints-for-nursing-students-8-320.jpg)







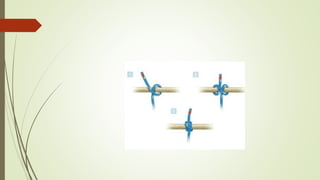
![EXTRIMITIES RESTRAINTS
[CLOVE HITCH RESTRAINTS]
To immobilize one or more EXTRIMITIES.
Same as elbow restraints.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation12-191209130450/85/Child-restraints-for-nursing-students-18-320.jpg)