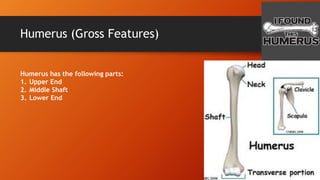
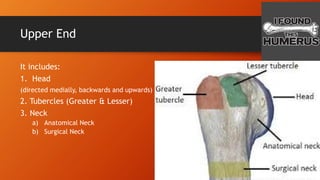
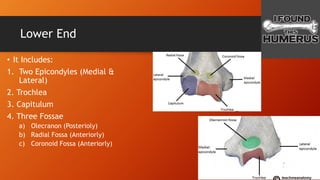
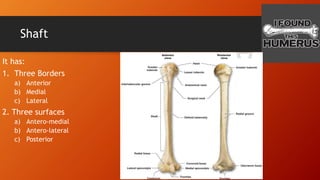
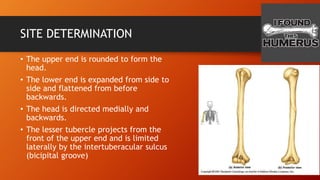
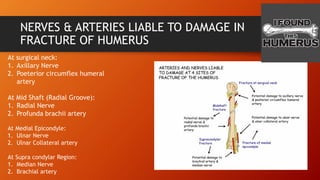
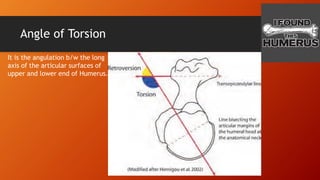
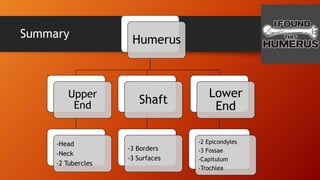
The humerus has an upper end with a head, neck, and two tubercles. The shaft has three borders and three surfaces. The lower end has two epicondyles, three fossae, a capitulum, and trochlea. Fractures of the humerus are common at the surgical neck, mid-shaft near the radial groove, medial epicondyle, and supracondylar region where the axillary nerve, radial nerve, ulnar nerve, brachial artery, and other structures are at risk of damage. The angle of torsion and carrying angle also have clinical significance.