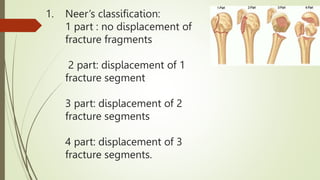
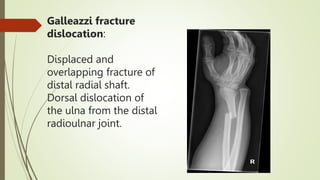
The document discusses various types of upper limb fractures and dislocations, including: shoulder dislocations like anterior and posterior dislocations; humeral head fractures; supracondylar fractures of the humerus; and forearm fractures such as Monteggia, Galeazzi, Colles, and scaphoid fractures. Key anatomical structures of the shoulder joint are described, as is Neer's classification system for proximal humeral fractures. Common signs on radiological imaging for different fractures are also outlined.