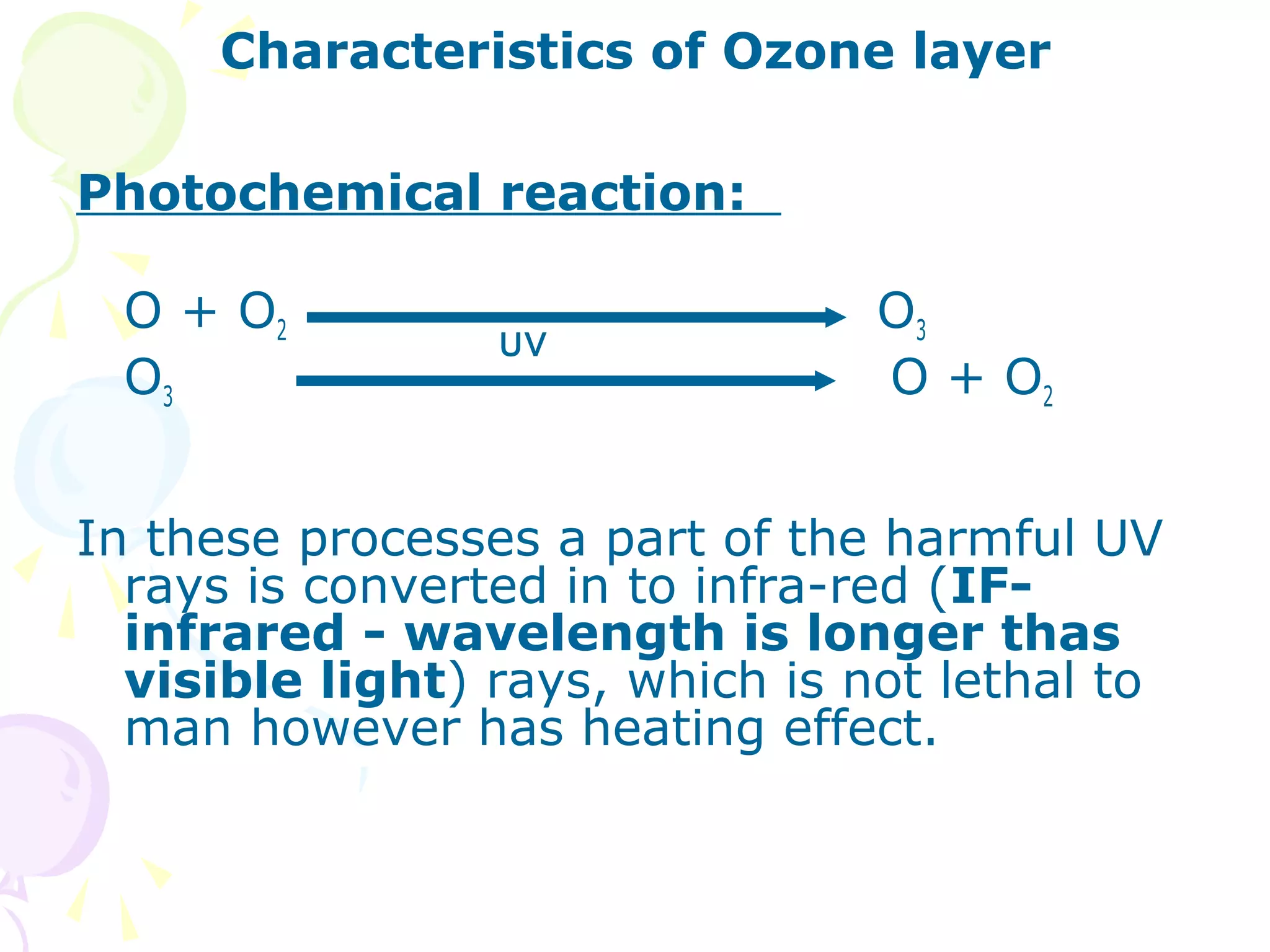
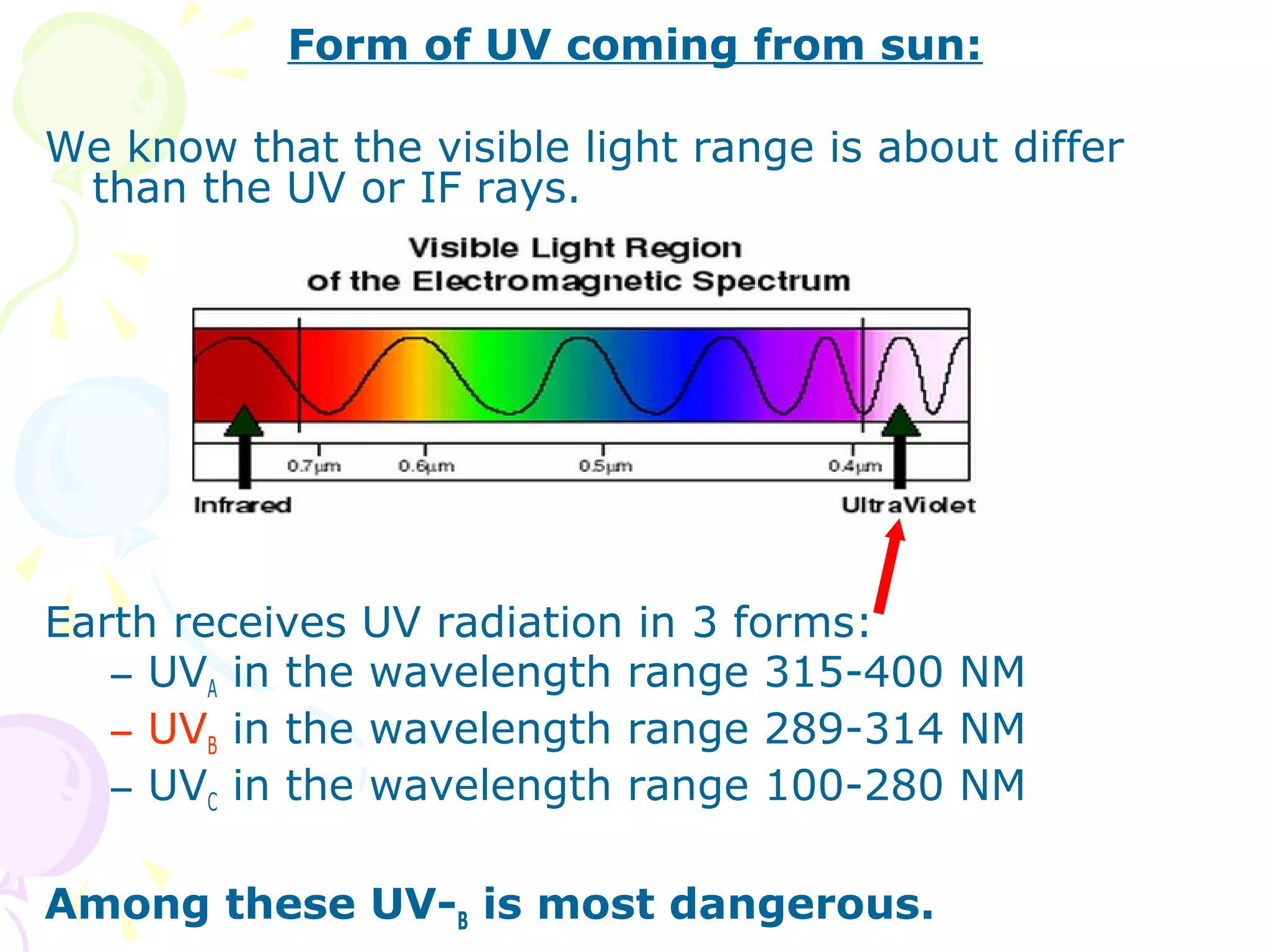
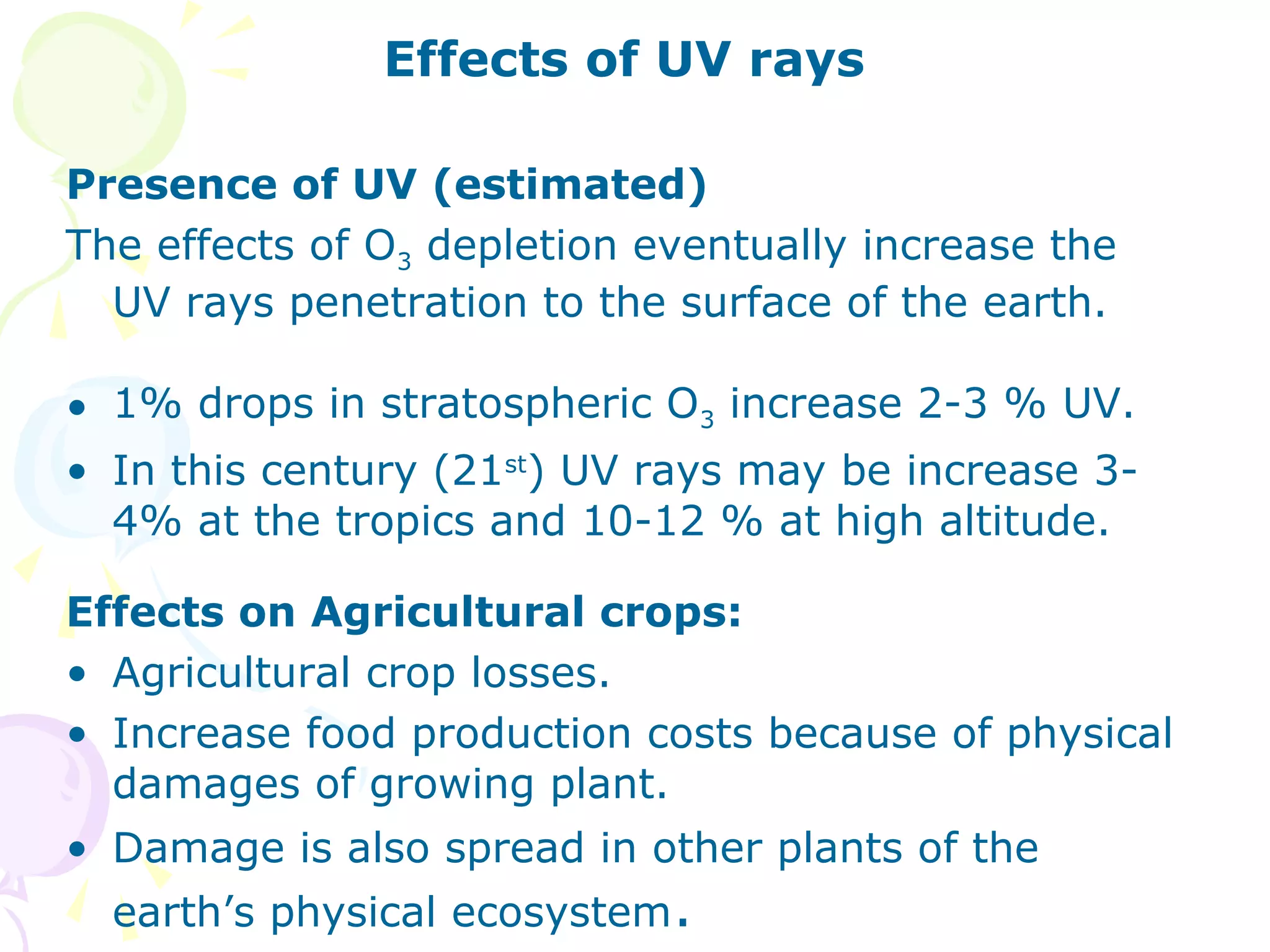
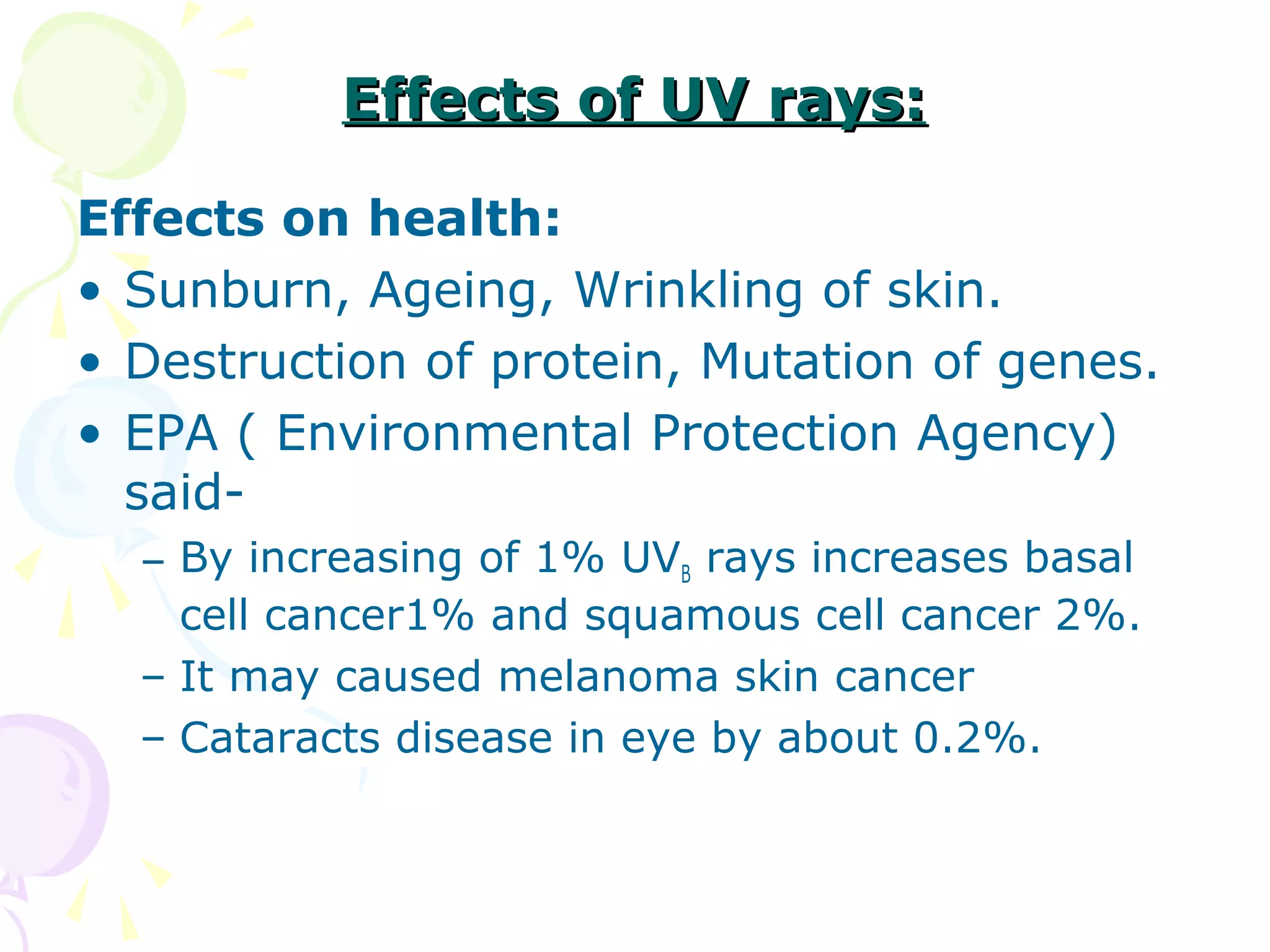
Ozone layer depletion occurs when ozone-depleting substances like CFCs break down ozone molecules in the stratosphere. This allows more ultraviolet radiation to reach the Earth's surface, increasing health and environmental risks. The ozone hole was first detected in 1975 and grew substantially in size through the 1980s and 1990s before stabilizing due to the Montreal Protocol banning CFCs. Global warming occurs when greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide trap heat in the lower atmosphere, increasing average surface and lower atmospheric temperatures globally over long periods of time. Both phenomena pose risks but international agreements have led to reductions in their drivers.