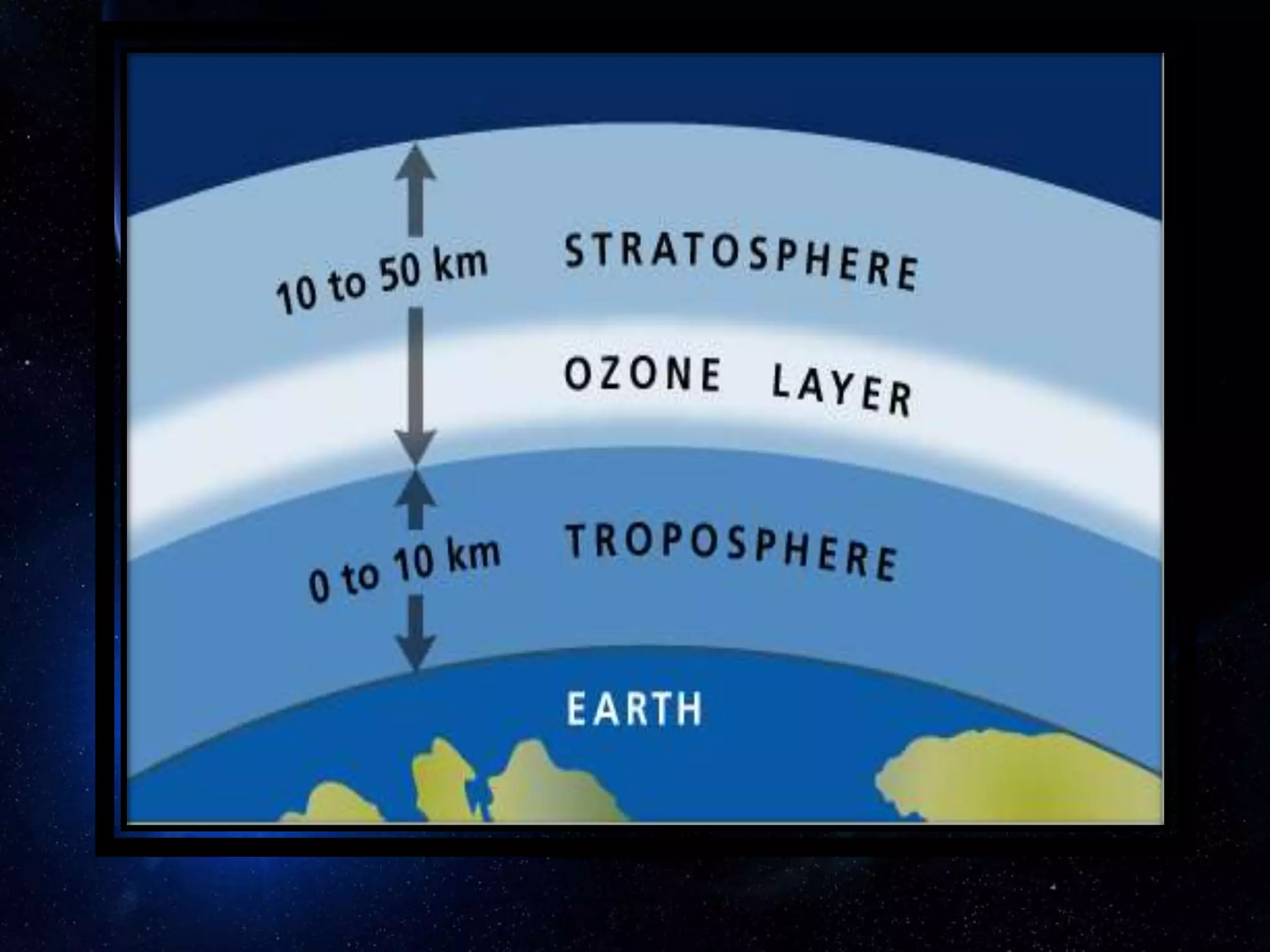
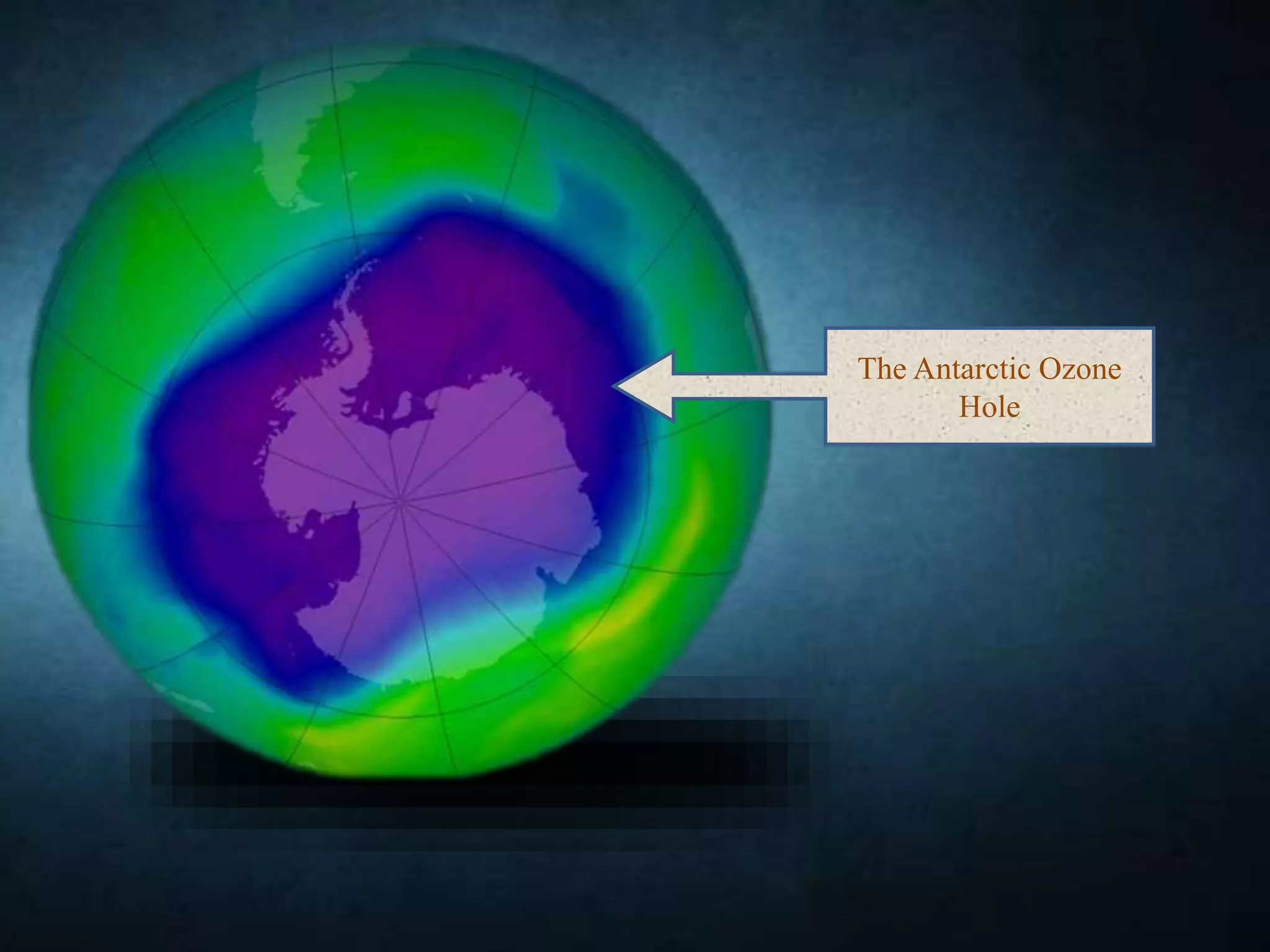
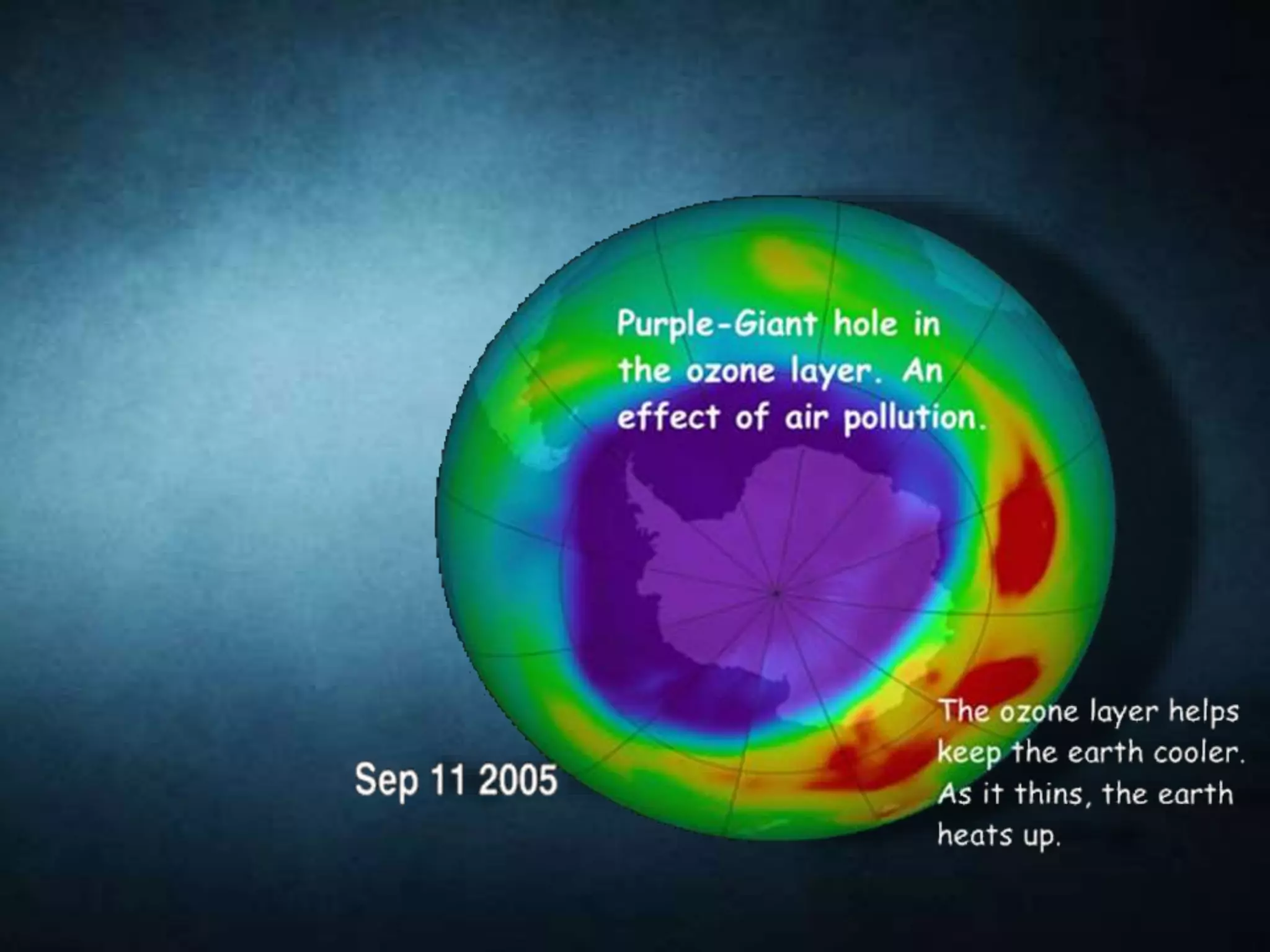
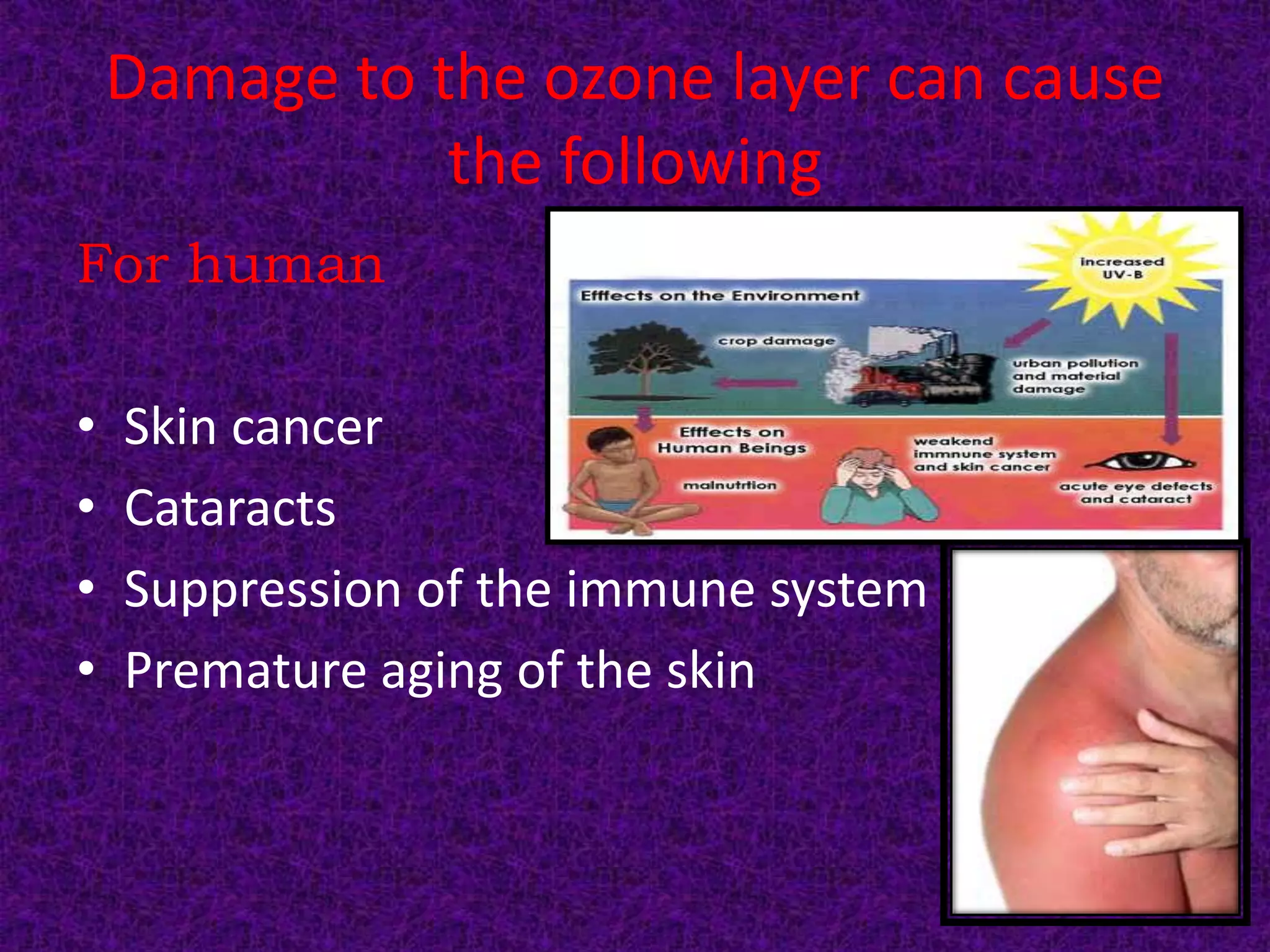
The document discusses the ozone layer, its importance in shielding the Earth from UV radiation, and the threats to it. It notes that ozone is found mainly in the stratosphere, where it forms the ozone layer between 6-30 miles above the surface. The ozone layer absorbs most of the sun's UV rays and plays a key role in atmospheric temperature. However, chlorofluorocarbons and other ozone-depleting substances have damaged the ozone layer, leading to the Antarctic ozone hole. This depletion increases UV levels and can harm both human health and the environment. International agreements like the Montreal Protocol have sought to phase out ozone-harming chemicals and find alternatives.