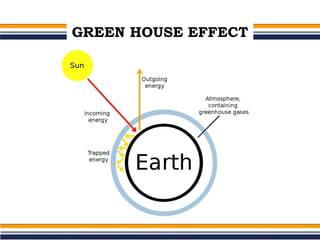
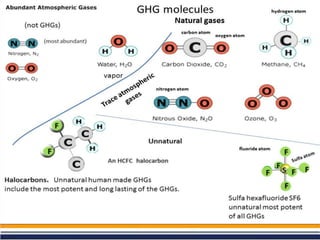
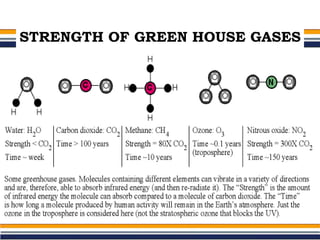
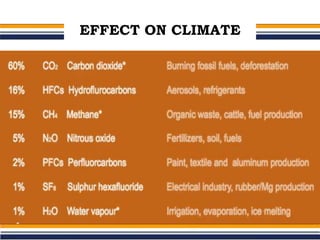
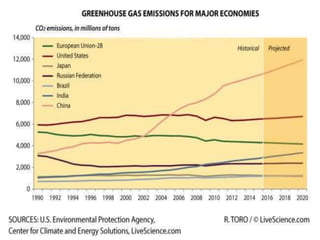
The greenhouse effect is a natural process where greenhouse gases trap infrared radiation, warming the Earth's surface and atmosphere. This effect can be intensified by human activities such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, leading to consequences like global warming and ozone depletion. Mitigation strategies include reducing greenhouse gas emissions, increasing energy efficiency, adopting renewable energy sources, and promoting sustainable land use.