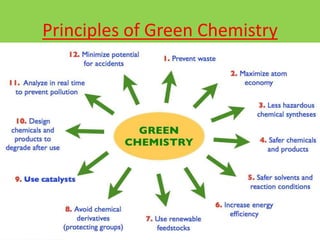
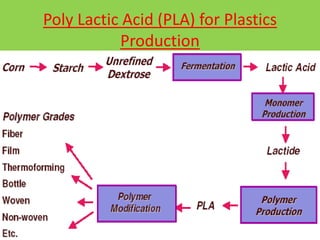
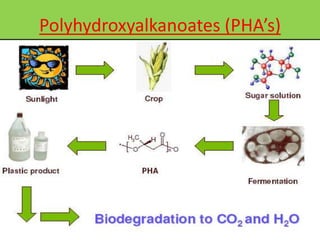
Green chemistry is the design of chemical products and processes that reduce or eliminate the use and generation of hazardous substances. It involves 12 principles that were established in 1998 to promote pollution prevention. Green chemistry has various applications in areas like plastics production and provides benefits such as reduced waste, costs, and health risks. It also helps address issues involving energy, resources, food supply, and toxins in the environment.