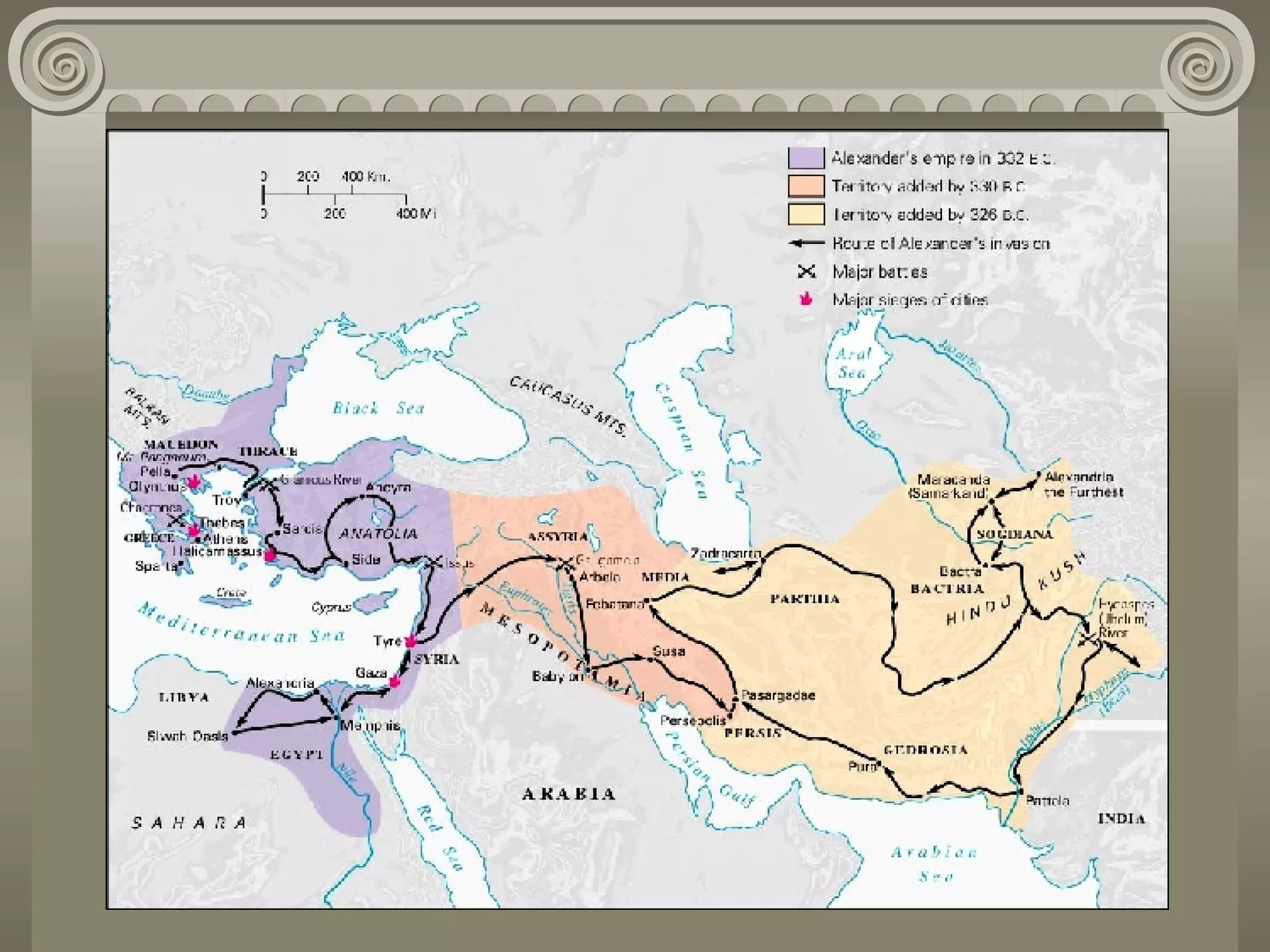
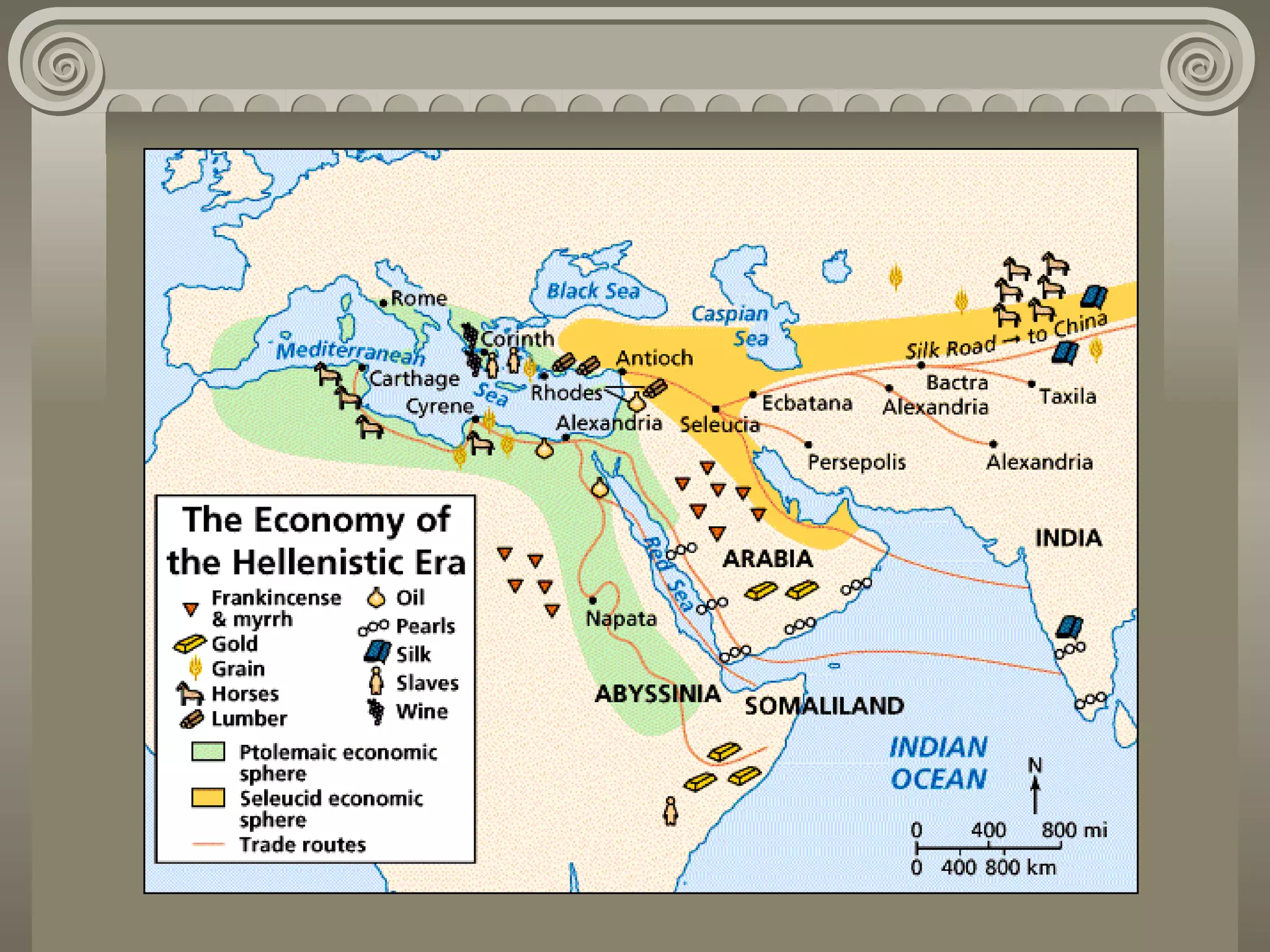
Ancient Greece had a profound influence on Western civilization through its contributions to language, science, mathematics, government, medicine, art, architecture, and history. The timeline began with the Minoan civilization on Crete around 2800 BCE. Various Greek city-states like Athens and Sparta rose to power between 800-500 BCE. The Classical Age saw a rise in democracy and culture under Athenian leadership and the conflicts with Persia and the Peloponnesian War between Sparta and Athens. Following the conquests of Alexander the Great, Greek culture spread throughout the known world in the Hellenistic Age from 324-100 BCE. Great philosophers like Socrates, Plato, and Aristotle developed the foundations of Western philosophy


















![Great Athenian Philosophers Socrates - Know thyself! - question everything - only the pursuit of goodness brings happiness. Plato - The Academy - the world of the FORMS - The Republic à philosopher-king Aristotle - the Lyceum - “Golden Mean” [everything in moderation] - Logic - Scientific method.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/greece-overview4250/75/Greece-Overview-21-2048.jpg)



