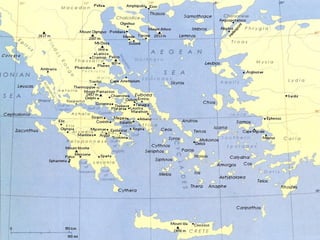
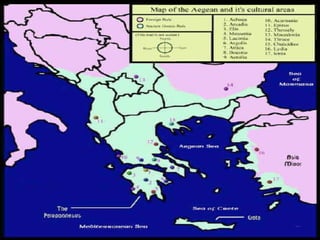
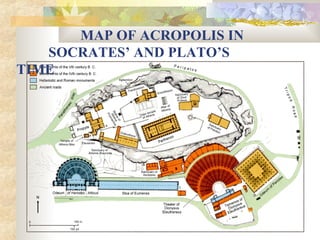
Greek civilization flourished between 1000 BC to 323 BC, originating in areas settled by ancient Greeks like the Greek peninsula, Cyprus, and parts of modern-day Turkey. It was characterized by the rise of independent city-states like Athens and Sparta, which practiced different forms of government. Athenian democracy and Spartan militarism were dominant. Greek culture had a significant influence on Western civilization through developments in philosophy, drama, architecture, science, and more. The civilization ended with the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the rise of Hellenistic empires.