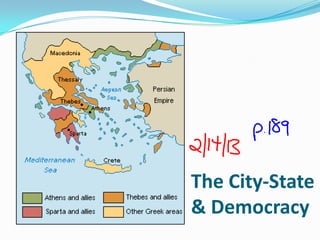
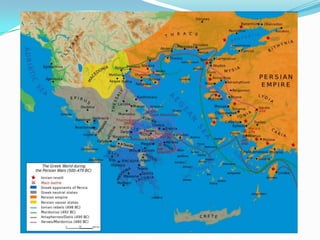
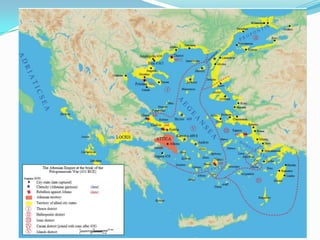
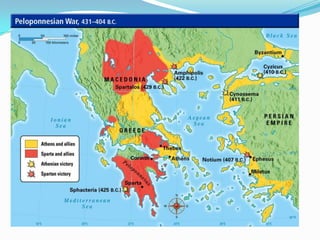
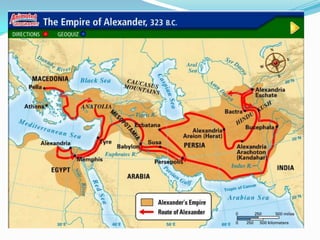
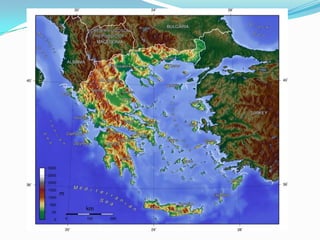
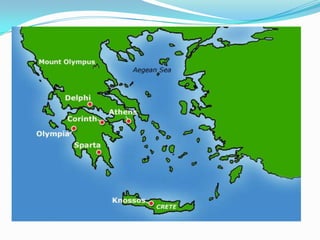
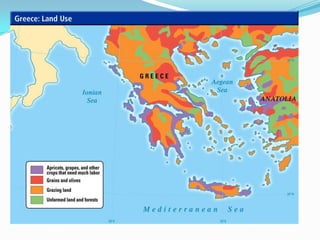
Greece's mountainous landscape with few rivers influenced the development of many independent city-states. The Mediterranean Sea and coastline encouraged seafaring and trade. During the Classical period in the 5th century BC, Athens developed a direct democracy while Sparta emphasized strict social hierarchy and military training. The two city-states fought in the Peloponnesian War, weakening Greece and allowing Philip II and his son Alexander the Great to conquer the region and spread Greek culture.














![Homer
Blind poet (c. [about]
8th Century BC)
Composed epics
Oral tradition
The Iliad
The Odyssey
Major influence in
Western literature](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ancientgreeceslideshare-130320132511-phpapp01/85/Ancient-greece-slide-share-19-320.jpg)