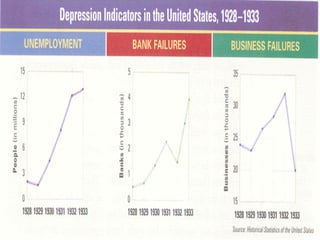
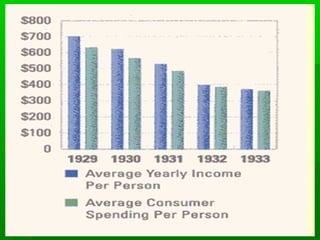
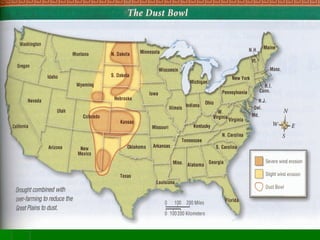
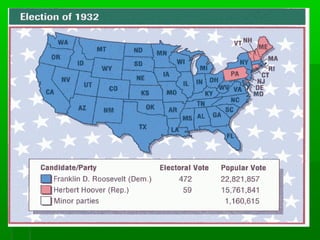
The Great Depression was caused by a combination of factors in the late 1920s and early 1930s, including unchecked speculation on credit, poor government policies, and a weak global economy recovering from World War I. The stock market crash of 1929 greatly exacerbated the economic crisis. As banks collapsed and millions lost their jobs, poverty and homelessness spread rapidly across the US. In response, President Franklin D. Roosevelt introduced his New Deal programs in the 1930s, which focused on relief, recovery, and reform through massive public works projects, the establishment of social security and financial regulations, and other initiatives aimed at revitalizing the economy. However, the Great Depression was not fully reversed until American involvement in World War II boosted industrial production.