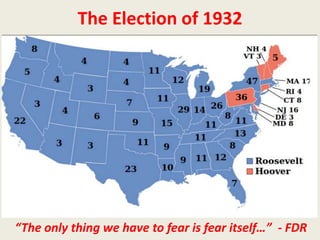
The document provides background on FDR and the New Deal in response to the Great Depression. It summarizes the purposes of the New Deal which were relief, recovery, and reform through government programs that provided jobs, food/money for those in need, built housing, regulated banks, and addressed issues like drought. It outlines several major New Deal programs and acts like the NRA, AAA, Social Security Act, and others aimed at industry, agriculture, labor reforms, and more. It also discusses criticisms from both radicals and conservatives and steps FDR took to protect the New Deal accomplishments.