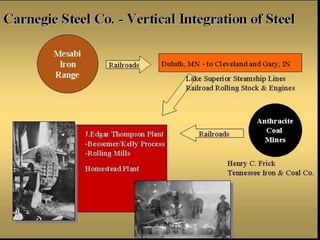
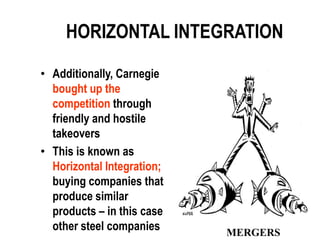
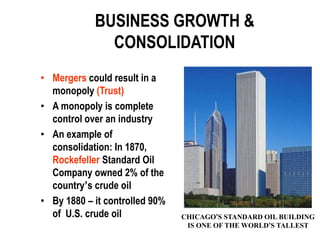
Andrew Carnegie dominated the steel industry in the late 19th century through vertical and horizontal integration strategies. He controlled raw materials, transportation, and bought out competitors to gain a near-monopoly on steel production in the United States. While criticized as "robber barons" for their cut-throat business practices, these industrialists like Carnegie and Rockefeller also engaged in generous philanthropy. However, the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890 aimed to limit the formation of monopolies but proved difficult to enforce against large businesses.