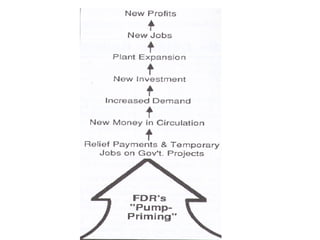
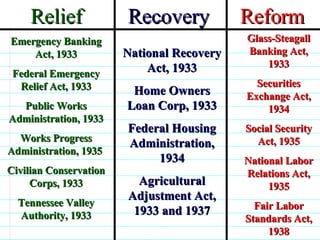
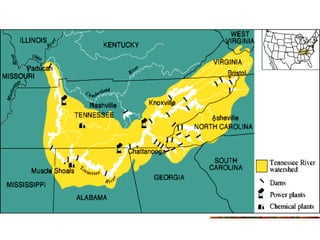
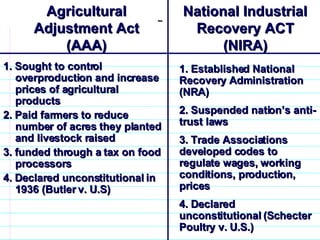
FDR and the New Deal. FDR was elected in 1932 with 57% of the popular vote on a platform of providing a "New Deal" for Americans suffering from the Great Depression. During his first 100 days in office, Congress passed major New Deal legislation including the AAA, NIRA, CCC, FERA, and Glass-Steagall Act to provide relief, recovery, and reform. However, the Supreme Court struck down some programs as exceeding Congressional authority.