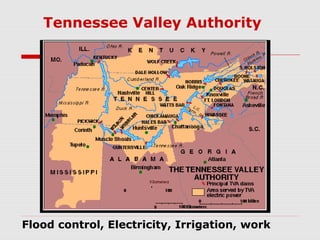
The document discusses the origins and causes of the Great Depression in the United States from 1929-1941, including extreme wealth inequality, overproduction, and a stock market crash. It then covers President Hoover's unsuccessful response and the growth of "Hoovervilles" before introducing Franklin D. Roosevelt and his "New Deal" programs designed to provide relief, recovery, and reform through massive government intervention, including the Works Progress Administration, Social Security, and initiatives to help farmers, the unemployed, and public works projects. The New Deal helped end the Depression but also significantly expanded the role of the federal government in the economy and society.