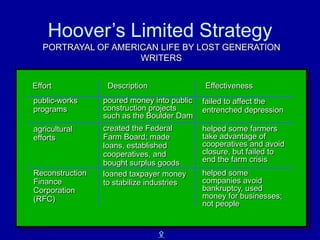
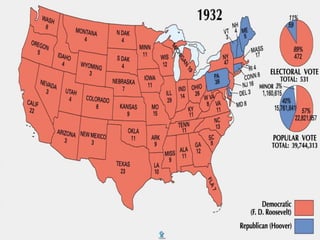
The document summarizes key aspects of the Great Depression and FDR's New Deal response in three parts. It first describes the economic downturn of the Great Depression from 1929-1941. Second, it outlines President Hoover's limited response which failed to alleviate widespread suffering. Third, it details how FDR was elected in 1932 promising a New Deal, and outlines major programs like the CCC, FDIC, AAA, and TVA that provided relief, jobs, and economic reforms to restore hope during the first 100 days of FDR's presidency.