1) The absorption of light by organic compounds involves the promotion of electrons from ground state to excited state molecular orbitals. Sigma electrons undergo σ-σ* transitions at shorter wavelengths while pi and non-bonding electrons undergo π-π* and n-π* transitions at longer wavelengths.
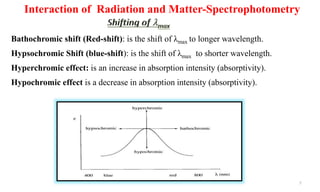
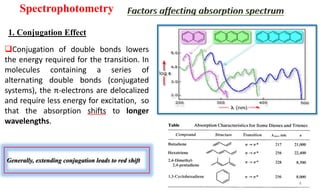
2) Chromophores are functional groups responsible for electronic transitions, imparting color. Auxochromes enhance absorption by chromophores through resonance. Conjugation and pH can shift absorption to longer wavelengths while dilution, solvents, and temperature can affect absorption spectra.
3) Spectrophotometry is widely used for quantitative analysis due to its sensitivity, selectivity, accuracy and ease. Both absorbing and non-absorbing
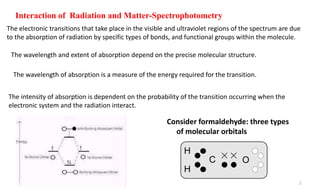

![The outer electrons in an organic molecule may occupy one of three different energy levels:
1- Sigma () electrons (single covalent bond (σ-bond): They are bonding electrons posses the
lowest energy level ( it is the most stable).
2- Pi () electrons: They are bonding electrons of higher energy than sigma electrons.
3- Non-bonding (n) electrons: They are of atomic orbital of hetero atoms (N,O, halogen or S)
which don’t participate in bonding, they usually occupy the highest level of ground state.
In excited state:
electrons under goes σ-σ* transition [high energy].
-electrons under goes -* transition, while,
n electrons under goes n- * or n-* transitions.
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spectroscopy-230527052122-8fc2b3f0/85/Spectroscopy-pptx-3-320.jpg)