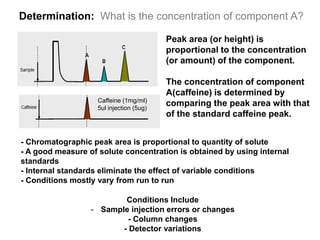
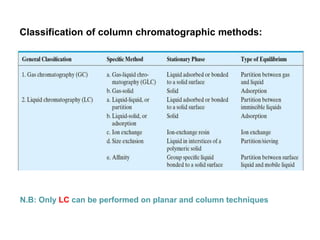
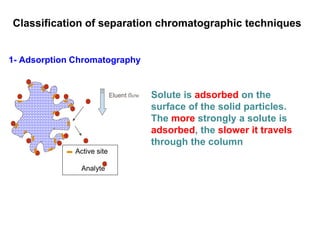
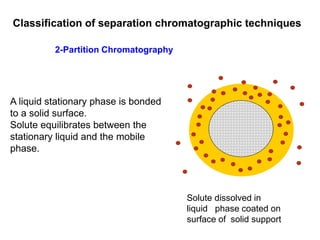
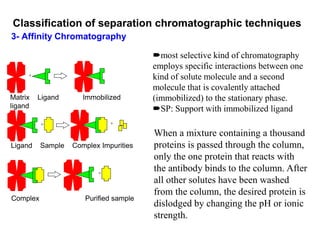
1. Quantitative analysis using chromatography relies on measuring either the height or area of analyte peaks. Peak area provides a better measure of concentration since it is unaffected by variations in column efficiency.
2. The concentration of an analyte is determined by comparing its peak area to that of a standard of known concentration. Internal standards are used to control for variable experimental conditions between runs.
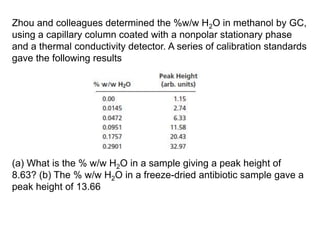
3. Calibration curves relate the detector response of external standards to their known concentrations. As long as injection volumes are identical, they provide accurate and precise results. Internal standards use the ratio of analyte to internal standard peak areas to normalize for variable conditions.


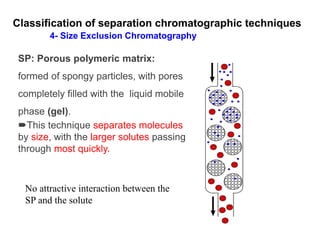
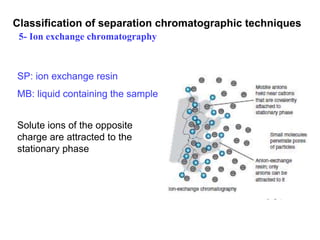





![Applications of Ion Exchange Chromatography
1- Water softening:
Removal of Ca2+, Mg2+ & other multivalent ions causing hardness
of water by filtration through a layer of strong cation resin.
2-Water demineralization:
Removal of cations & anions dissolved in water. Usually carried by
the two step technique in which two columns are used in
sequence.
3- Neutralization:
Cationic exchanger in [H+] can be used to neutralize alkali hydroxide
& anionic exchanger in [OH-] form to neutralize the acidity.
4- Separation of electrolytes from non-electrolytes.
5- Separation of carbohydrates & their derivatives:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chromatography-230623162731-7f8ba64d/85/Chromatography-ppt-24-320.jpg)