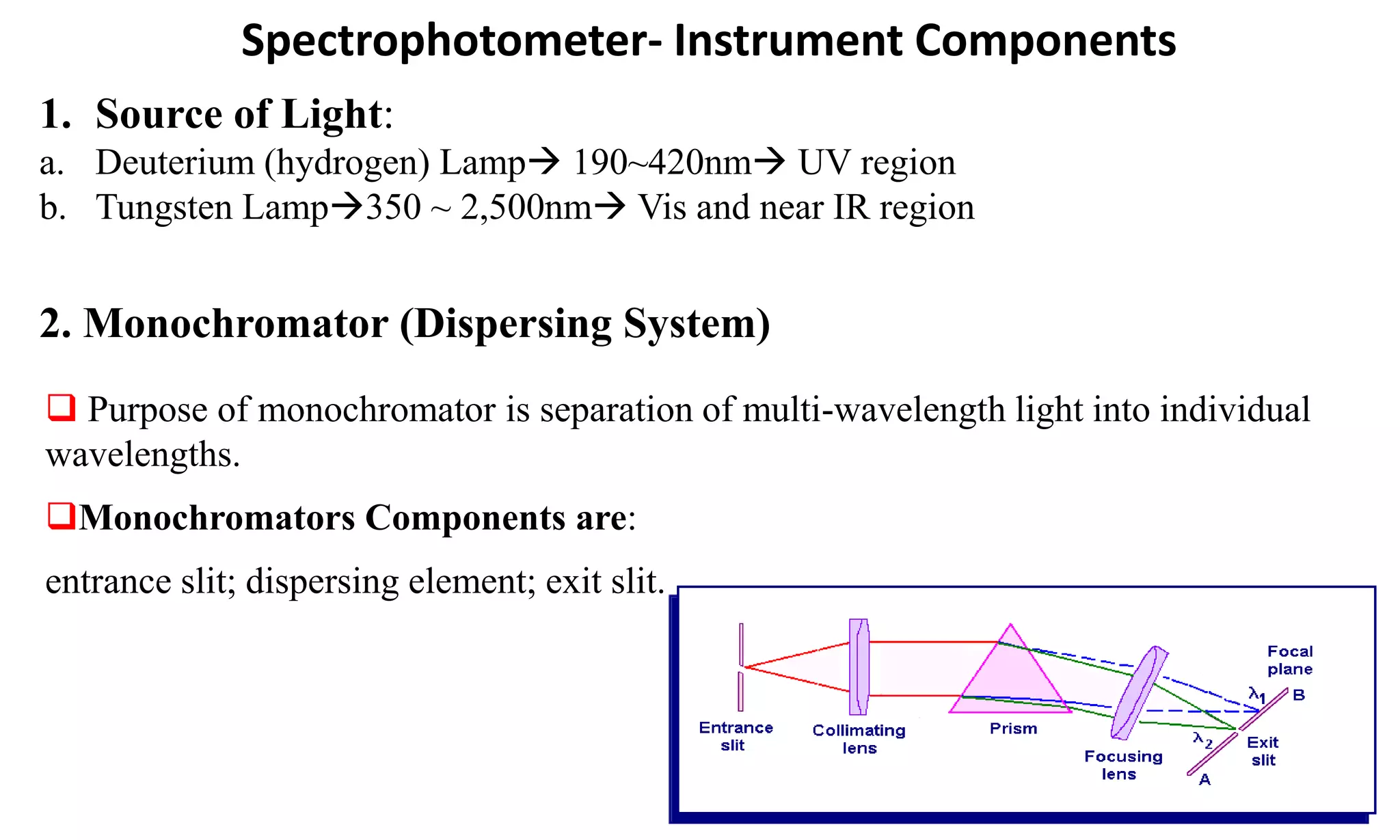
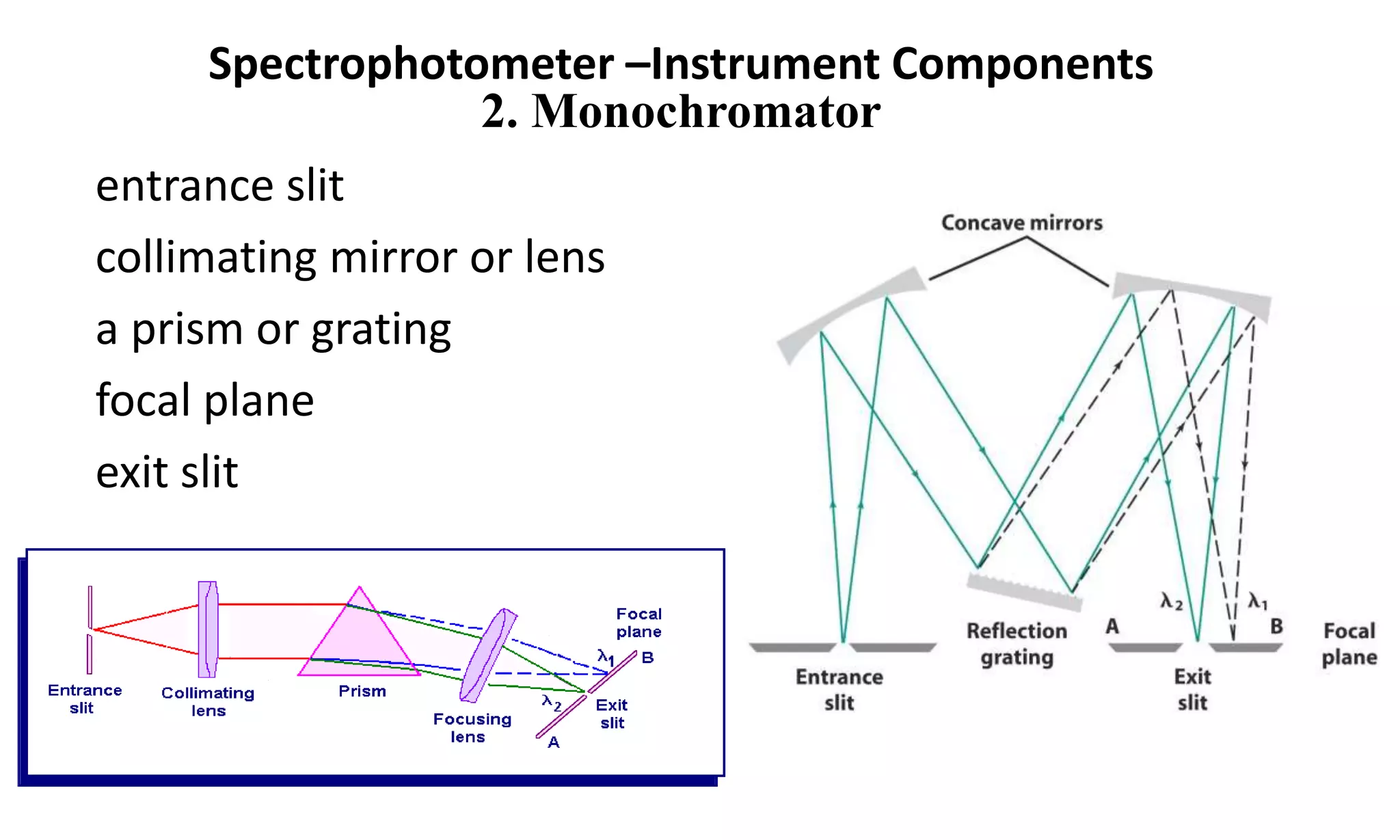
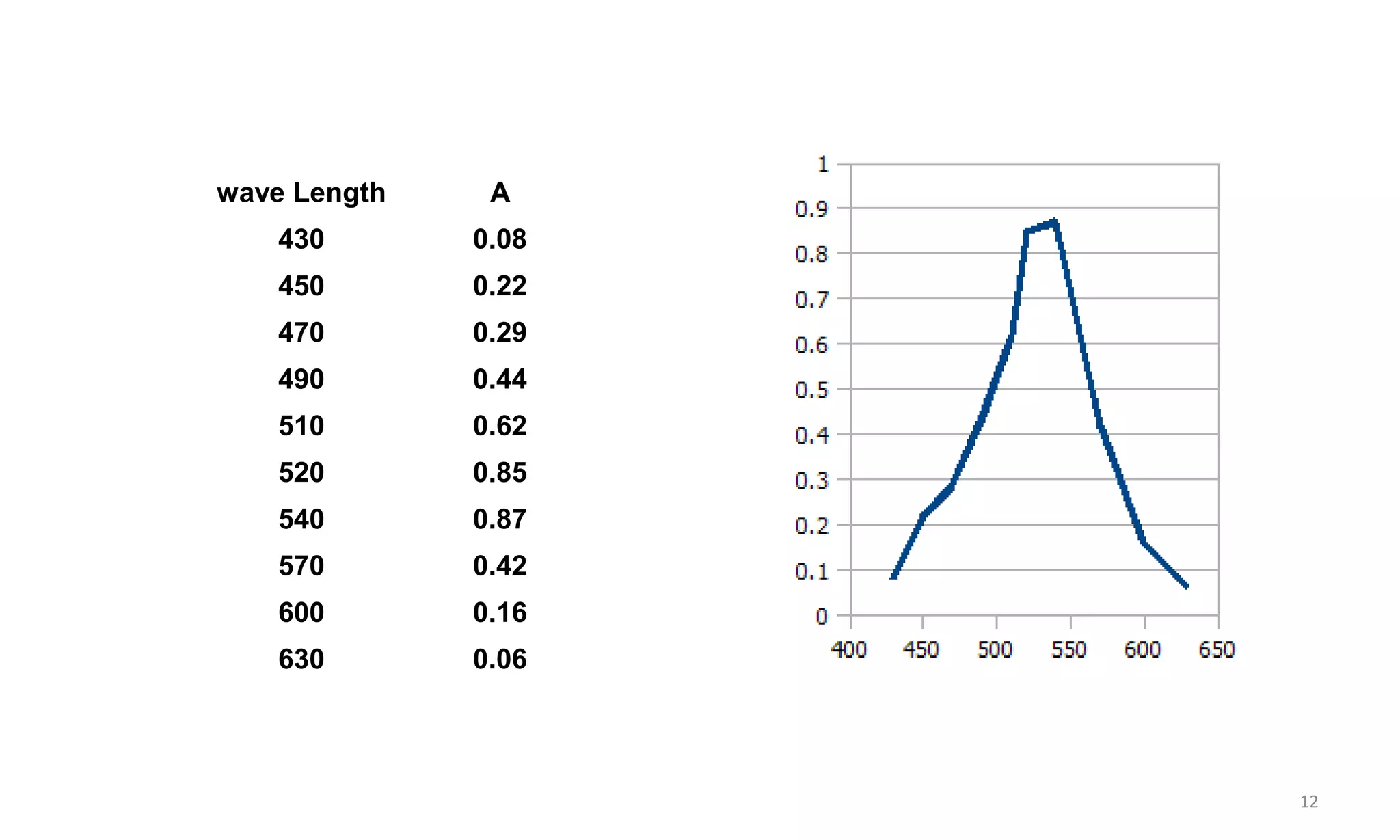
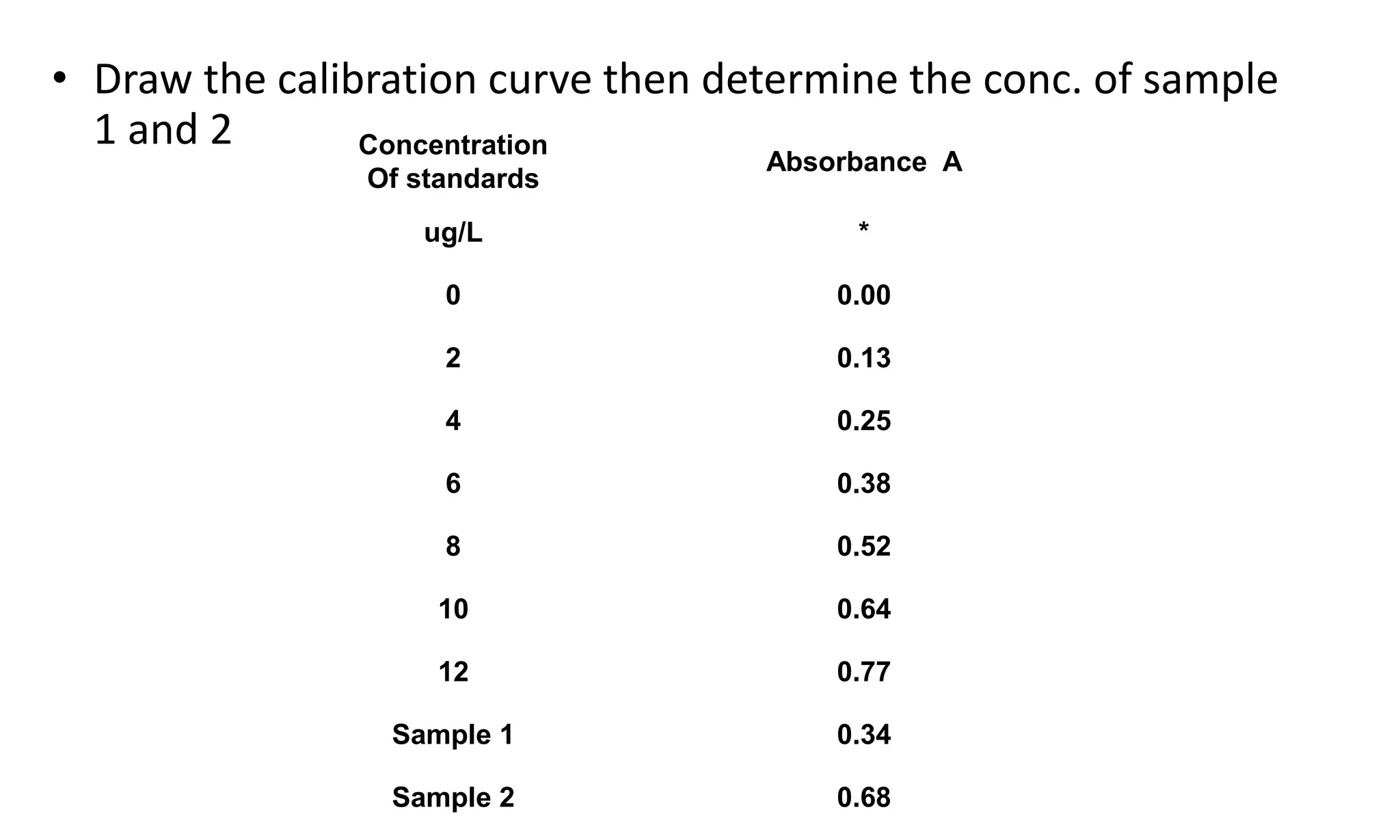
A spectrophotometer measures the transmittance or absorbance of light through a sample as a function of wavelength. It consists of five main components: a radiant energy source, a monochromator to select wavelengths, a sample compartment, a detector, and a recorder. The monochromator separates light into individual wavelengths using filters, prisms, or diffraction gratings. The detector converts the transmitted light intensity into an electrical signal proportional to absorbance. Spectrophotometers can operate in single or double beam mode for measuring samples.