Embed presentation
Download to read offline


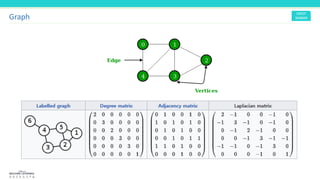

![Adjacency matrix
Node feature
DNN
Ideal algorithm?
[ Naïve Approach ]
1. # of parameters
2. Invariant to node ordering
3. Locality
Graph Convolutional Network](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcn-200601151804/85/Graph-Convolutional-Network-10-320.jpg)

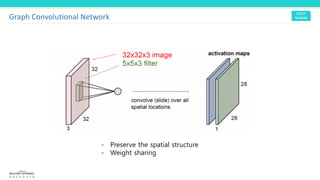
![[ Input ]
[ Output ]
[ NN layer]
Graph Convolutional Network](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcn-200601151804/85/Graph-Convolutional-Network-13-320.jpg)
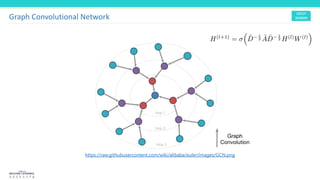
![[ Layer-wise propagation rule ]
Graph Convolutional Network
With weight matix W(l) of dimension F(l) x F(l+1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcn-200601151804/85/Graph-Convolutional-Network-14-320.jpg)
![[ Layer-wise propagation rule ]
Graph Convolutional Network
symmetric normalized Laplacian matrix form](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcn-200601151804/85/Graph-Convolutional-Network-15-320.jpg)
![[ Convolution on Graphs? ]
Chebyshev polynomial
Eigen value, vector,
decomposition
Fourier transform
Normalized Graph Laplacian
…….
Graph Convolutional Network
[ Fast Approximate Convolutions on Graphs]
= [ Graph Fourier Transform from Laplacian Matrix ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcn-200601151804/85/Graph-Convolutional-Network-16-320.jpg)

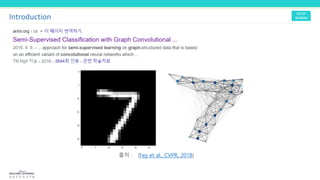
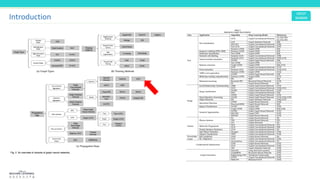
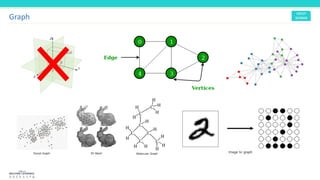
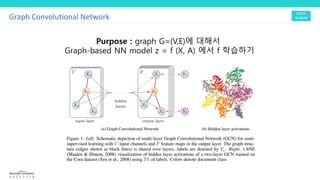
This document discusses graph convolutional networks (GCNs), which are neural network models for graph-structured data. GCNs aim to learn functions on graphs by preserving the graph's spatial structure and enabling weight sharing. The document outlines the basic components of a GCN, including the adjacency matrix, node features, and application of deep neural network layers. It also notes some challenges with applying convolutions to graphs and discusses approaches like using the graph Fourier transform based on the Laplacian matrix.









![Adjacency matrix
Node feature
DNN
Ideal algorithm?
[ Naïve Approach ]
1. # of parameters
2. Invariant to node ordering
3. Locality
Graph Convolutional Network](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcn-200601151804/85/Graph-Convolutional-Network-10-320.jpg)


![[ Input ]
[ Output ]
[ NN layer]
Graph Convolutional Network](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcn-200601151804/85/Graph-Convolutional-Network-13-320.jpg)
![[ Layer-wise propagation rule ]
Graph Convolutional Network
With weight matix W(l) of dimension F(l) x F(l+1)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcn-200601151804/85/Graph-Convolutional-Network-14-320.jpg)
![[ Layer-wise propagation rule ]
Graph Convolutional Network
symmetric normalized Laplacian matrix form](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcn-200601151804/85/Graph-Convolutional-Network-15-320.jpg)
![[ Convolution on Graphs? ]
Chebyshev polynomial
Eigen value, vector,
decomposition
Fourier transform
Normalized Graph Laplacian
…….
Graph Convolutional Network
[ Fast Approximate Convolutions on Graphs]
= [ Graph Fourier Transform from Laplacian Matrix ]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gcn-200601151804/85/Graph-Convolutional-Network-16-320.jpg)


