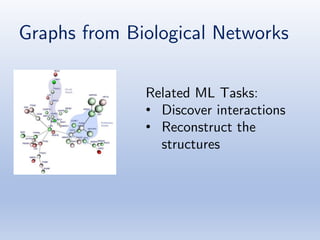
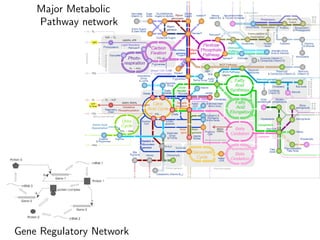
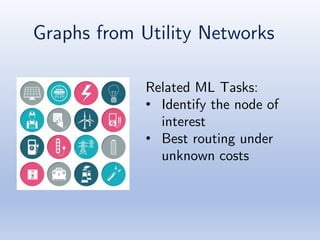
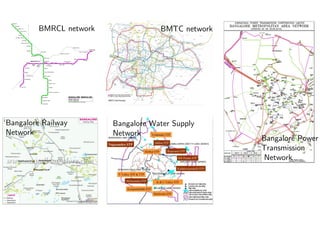
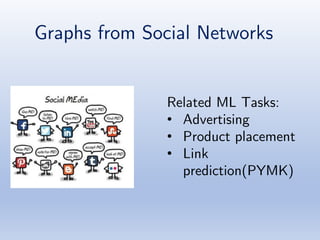
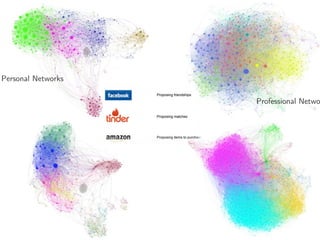
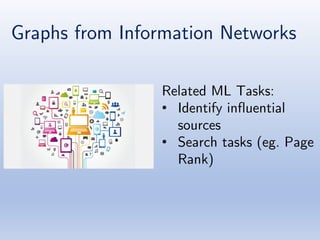
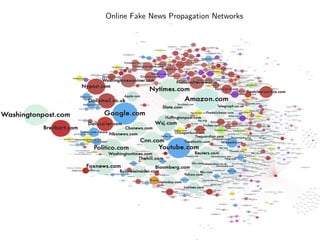
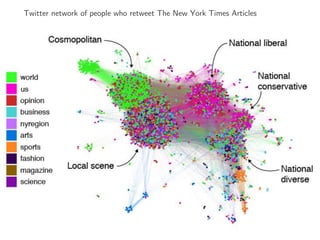
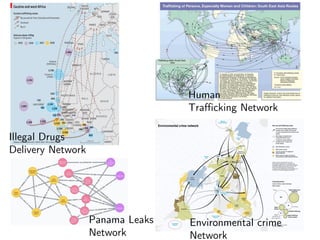
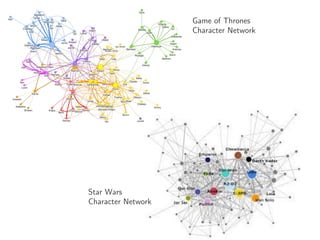
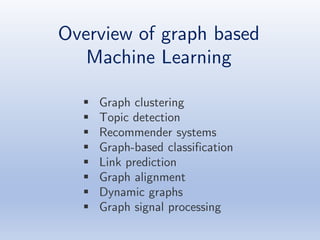
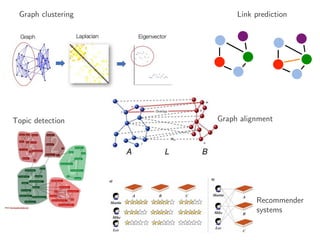
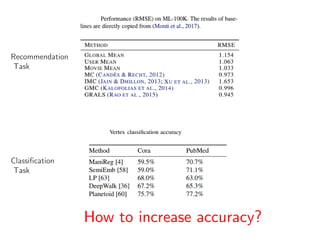
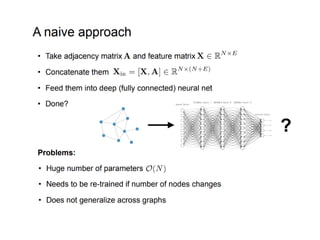
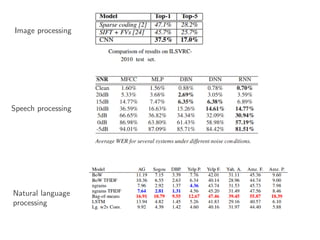
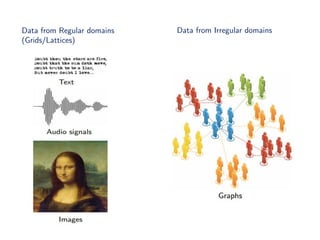
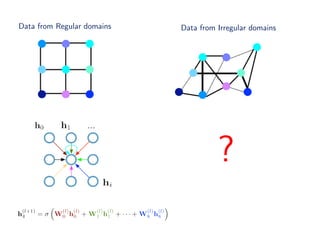
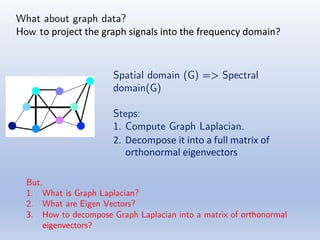
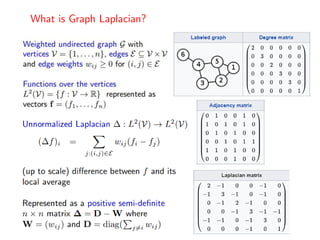
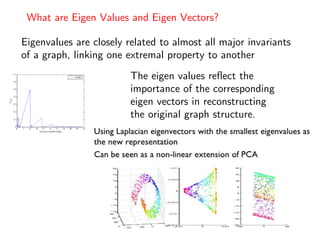
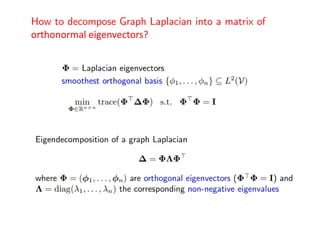
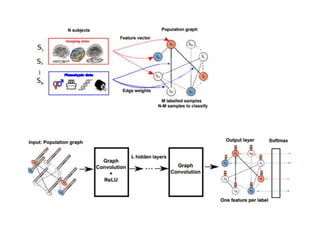
The document discusses deep learning applications on graphs, covering various types of networks including social, biological, and utility networks. It features an overview of graph-based machine learning techniques, such as spectral graph convolutions and applications of graph convolutional networks, including semi-supervised learning and distance metric learning. Recent developments in relational deep learning and multiple references for further exploration of the topic are also included.











![References:
• Deep Feature Learning for Graphs
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.08829.pdf
• Learning Convolutional Neural Networks for Graphs
http://proceedings.mlr.press/v48/niepert16.pdf
• Deep Learning on Graphs with Graph Convolutional Networks [ppt]
http://deeploria.gforge.inria.fr/thomasTalk.pdf
• Graph Convolutional Networks [blog]
http://tkipf.github.io/graph-convolutional-networks/
• Geometric deep learning: going beyond Euclidean data
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.08097.pdf
• Convolutional Neural Networks on Graphs [ppt]
http://helper.ipam.ucla.edu/publications/dlt2018/dlt2018_14506.pdf
• CayleyNets: Graph Convolutional Neural Networks with Complex Rational Spectral Filters
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.07664.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlforgraphsdlblr-180618010205/85/Deep-Learning-for-Graphs-56-320.jpg)
![• Deep Geometric Matrix Completion [ppt]
http://helper.ipam.ucla.edu/publications/dlt2018/dlt2018_14552.pdf
• On Computational Hardness and Graph Neural Networks
http://helper.ipam.ucla.edu/publications/dlt2018/dlt2018_14508.pdf
• Machine Learning Meets Geometry [ppt]
http://geometry.cs.ucl.ac.uk/SGP2017/slides/Rodola_MachineLearningMeetsGeometry_SGP.pdf
• Geometric deep learning on graphs and manifolds [ppt]
http://geometricdeeplearning.com/slides/NIPS-GDL.pdf
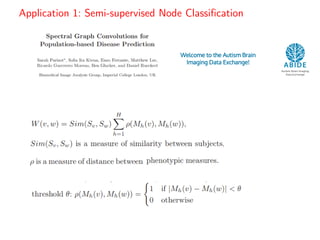
• Spectral Graph Convolutions for Population-based Disease Prediction
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1703.03020.pdf .
[Code@ https://github.com/parisots/population-gcn]
• Semi-supervised Classification with Graph Convolutional Networks
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1609.02907.pdf
• Geometric deep learning on graphs and manifolds using mixture model CNNs
https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.08402.pdf](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlforgraphsdlblr-180618010205/85/Deep-Learning-for-Graphs-57-320.jpg)
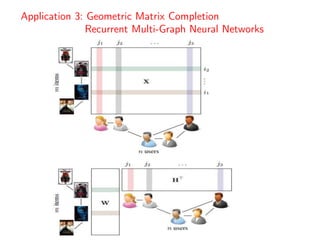
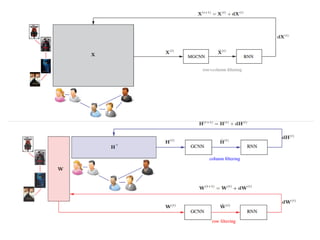
![• Geometric Matrix Completion with Recurrent Multi-Graph Neural Networks
• https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.06803v1.pdf
• [Code@ https://github.com/fmonti/mgcnn]
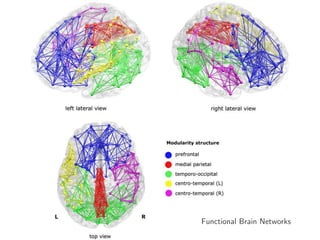
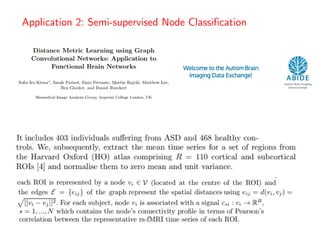
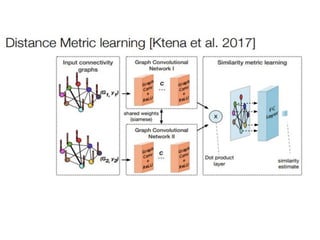
• Distance Metric Learning using Graph Convolutional Networks Application to Functional
Brain Networks
• https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.02161
• [Code@ https://github.com/sk1712/gcn_metric_learning]
Other code links:
• A tutorial on Graph Convolutional Neural Networks
https://github.com/dbusbridge/gcn_tutorial
• Graph-based Neural Networks
https://github.com/sungyongs/graph-based-nn
https://github.com/LeeDoYup/Graph-Convolutional-Networks
https://github.com/fps7806/Graph-CNN
• FastGCN: Fast Learning with Graph Convolutional Networks via Importance Sampling
https://github.com/matenure/FastGCN
• Graph Convolutional Networks in PyTorch
https://github.com/tkipf/pygcn
• Graph Convolutional Networks
https://github.com/tkipf/gcn
Note: The images/equations used in the slides are borrowed from either Google images, Wikipedia or from respective
research papers/presentations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dlforgraphsdlblr-180618010205/85/Deep-Learning-for-Graphs-58-320.jpg)