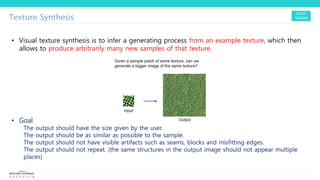
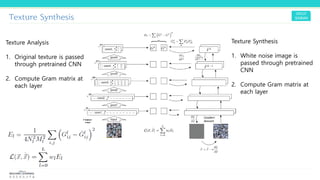
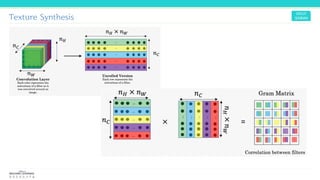
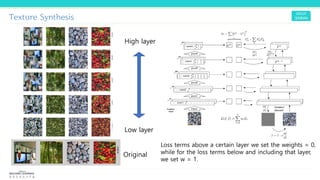
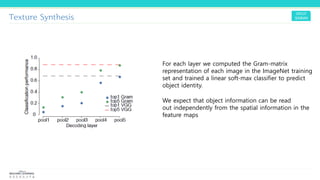
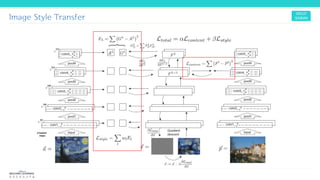
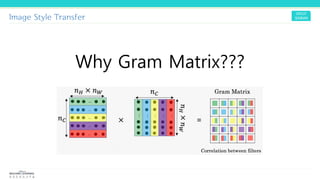
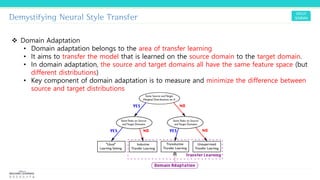
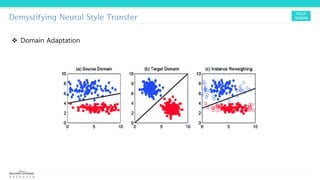
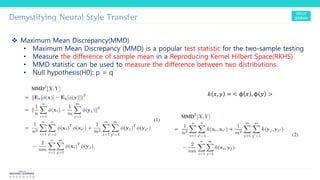
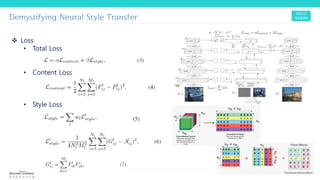
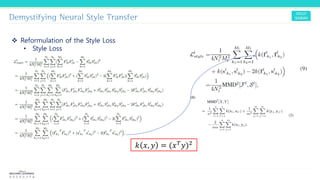
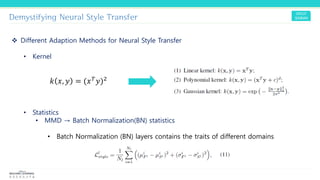
Texture synthesis aims to produce new texture samples from an example that are similar but not repetitive. It analyzes the example using a CNN to compute gram matrices representing the texture at different layers, then synthesizes new textures by passing noise through the CNN and minimizing differences from the example's gram matrices. Style transfer extends this to merge the texture of one image onto the content of another by matching gram matrices between layers to transfer style while preserving content. It has been shown that style and content are separable in CNN representations. Style transfer can be viewed as a type of domain adaptation between content and style domains.