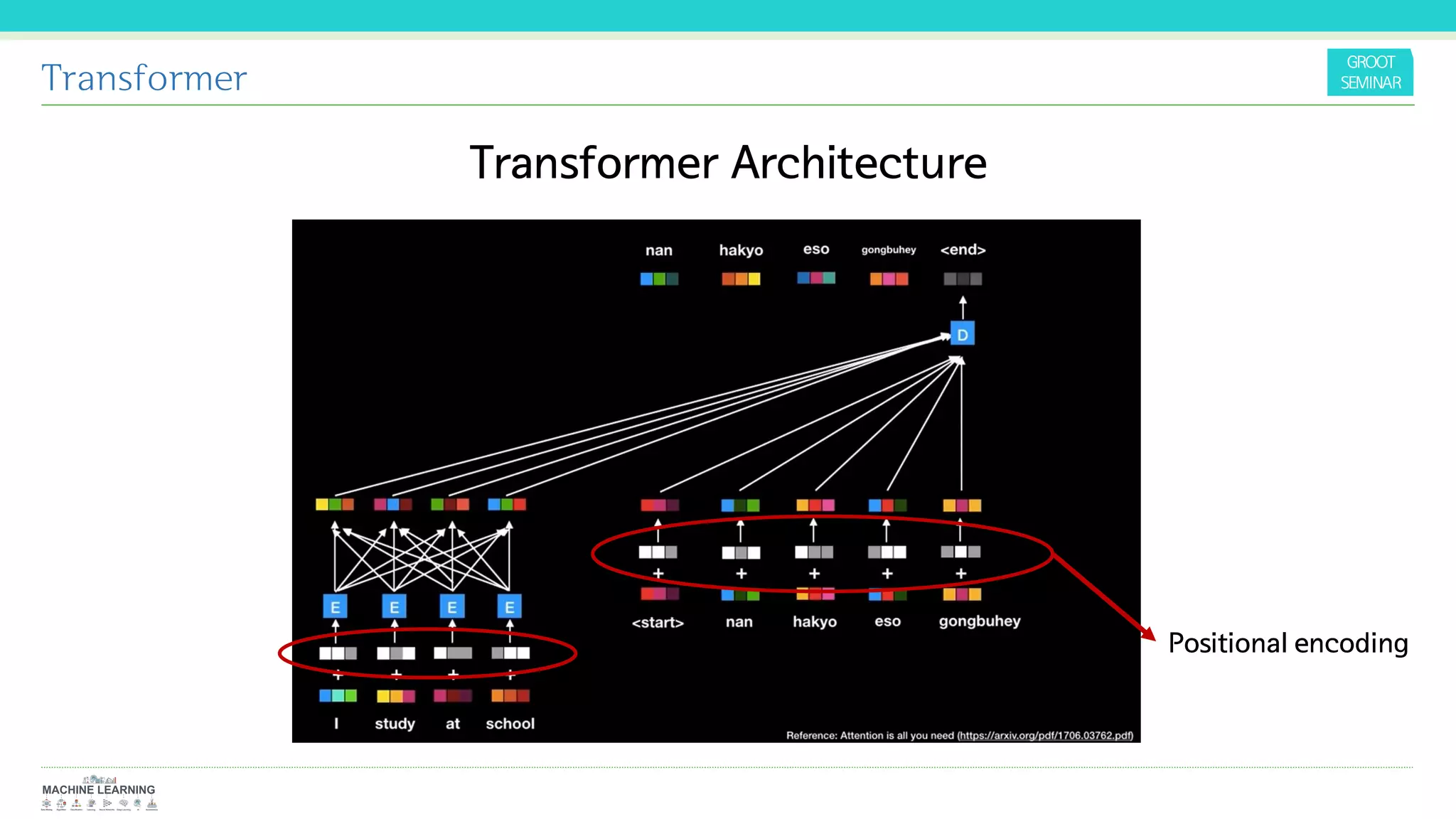
The document discusses Ashish Vaswani's talk on the Transformer architecture, highlighting its use of attention mechanisms for sequence transduction tasks. The proposed model outperforms traditional recurrent and convolutional neural networks in machine translation and other applications by enhancing parallelization and reducing training time. It introduces the concept of self-attention and positional encoding, showcasing significant improvements in translation quality.










![Transformer
Why not RNN?
This inherently sequential nature precludes parallelization within training
examples, which becomes critical at longer sequence lengths, as memory
constraints limit batching across examples. Recent work has achieved
significant improvements in computational efficiency through factorization
tricks [21] and conditional computation [32], while also improving model
performance in case of the latter. The fundamental constraint of
sequential computation, however, remains.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/attentionisallyouneed-groot-200501100555/75/Attention-Is-All-You-Need-11-2048.jpg)