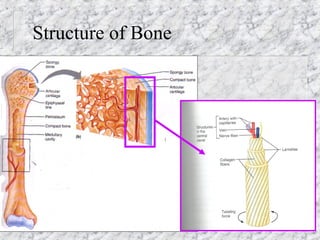
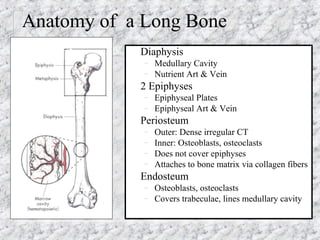
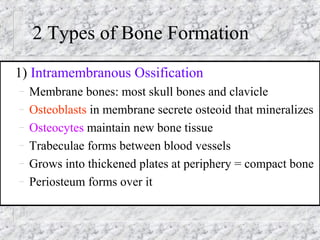
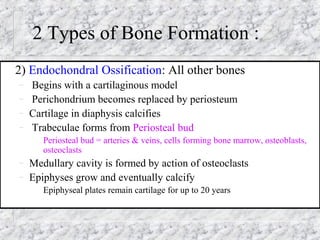
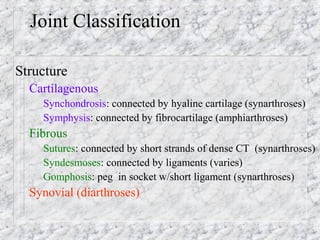
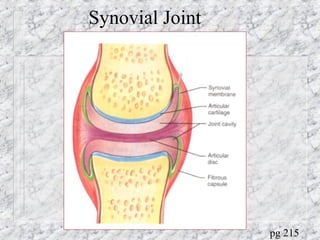
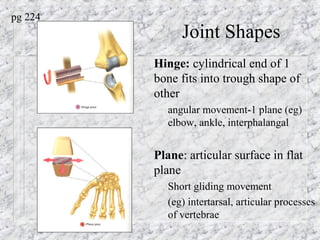
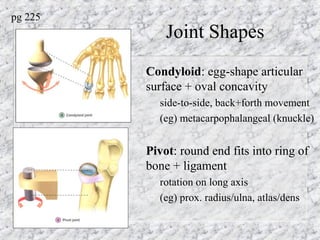
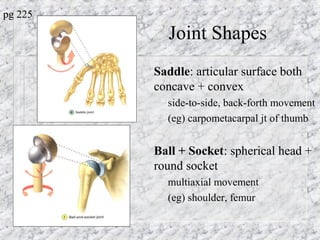
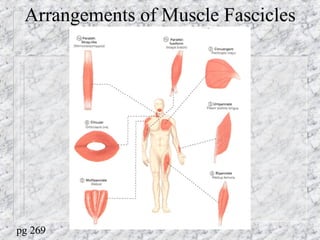
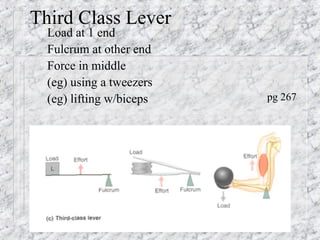
Bones provide structure, protect organs, allow movement, and store minerals. The 206 bones in the human body develop through two processes - intramembranous ossification and endochondral ossification. Bones continuously remodel through the actions of osteoclasts which break down bone and osteoblasts which build new bone. Joints connect bones and allow varying degrees of movement. The three types are synarthroses, amphiarthroses, and diarthroses. Muscles connect to bones via tendons and contract to create movement by applying force at leverage points. They work antagonistically and synergistically to move the body.