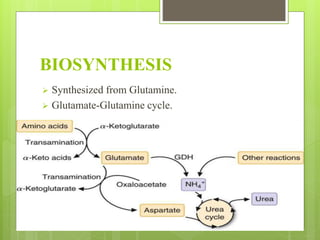
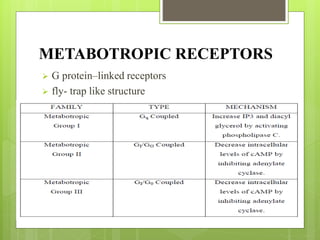
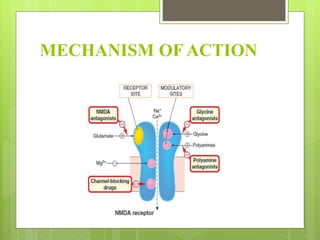
Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and is involved in cognitive functions like learning and memory. It has two major classes of receptors - ionotropic and metabotropic receptors. Glutamate is synthesized from glutamine via the glutamate-glutamine cycle and stored in vesicles for release. It is transported back into glial cells via glutamate transporters and converted back to glutamine. Drugs can target ionotropic receptors as antagonists to treat conditions caused by glutamate toxicity like neurodegeneration, ischemia and seizures.