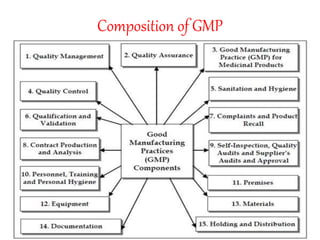
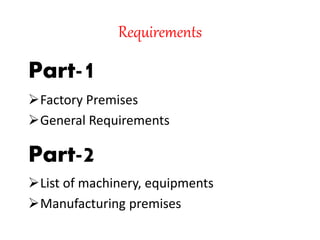
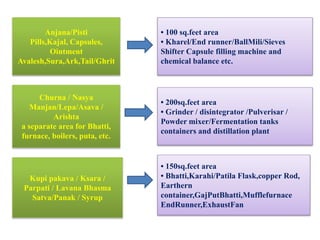
The document discusses Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) for herbal medicines in Indian systems of medicine. It outlines the key requirements for GMP compliance, including factory premises requirements, manufacturing processes, equipment, quality control, training, documentation, labeling and packing. The objectives of GMP are to ensure authentic and quality raw materials are used, manufacturing processes are standardized, and finished products meet predefined specifications to ensure consistent quality and minimize contamination and errors.