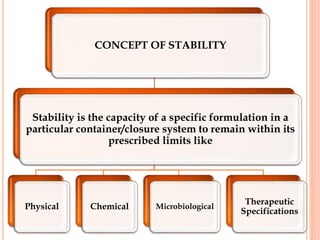
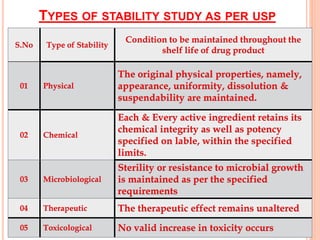
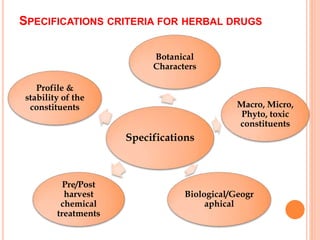
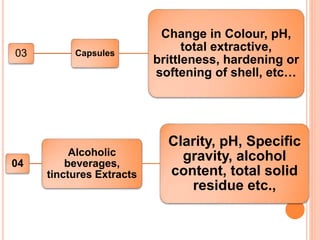
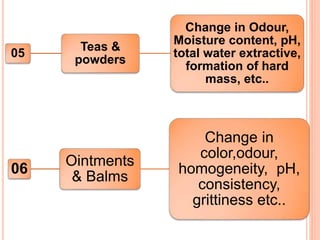
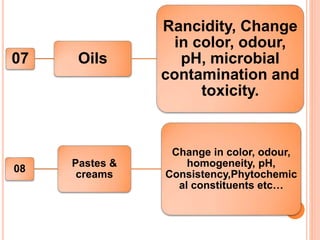
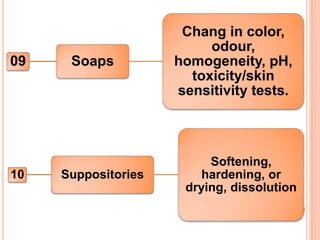
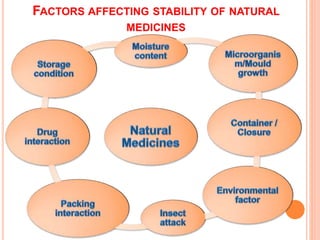
This document discusses stability testing of herbal drugs. Stability is defined as the capacity of a drug to remain within established specifications limits to maintain its identity, quality and purity throughout its retest or expiration period. Stability testing helps determine a product's shelf life and suitable formulations, excipients, and packaging. It ensures product quality and safety for patients. Types of stability studies include physical, chemical, microbiological, and therapeutic stability testing. The document outlines specifications criteria, testing methods like real-time and accelerated testing, protocols, recommended tests for different dosage forms, and factors affecting stability of herbal medicines like physical and chemical instability, complexity, and drug interactions.