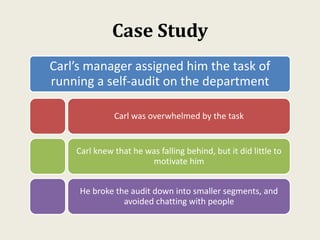
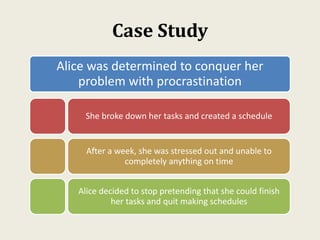
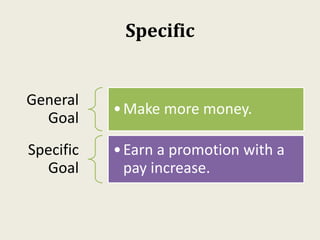
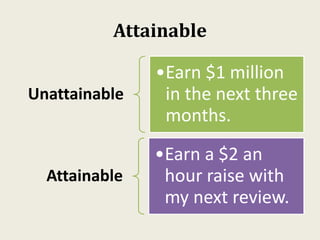
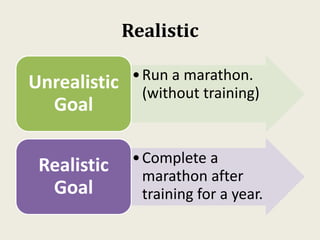
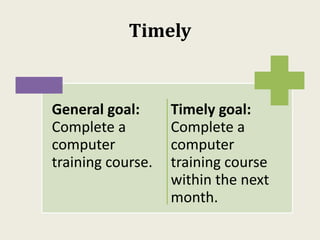
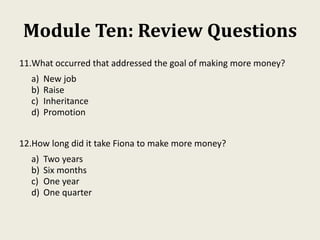
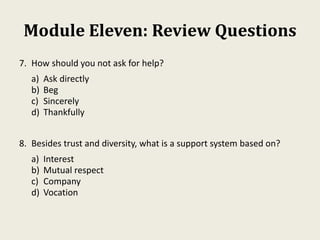
Sarah wanted to stay motivated to achieve her goals. She remembered positive past experiences that motivated her. She wrote down her goals using empowering language in the present tense. Sarah also gamified her goals by assigning points to tasks and tracking progress. This helped her see accomplishments and areas to focus on, keeping her motivated to work towards her goals.