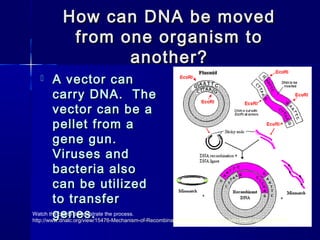
Genetically modified foods are foods that have had their DNA altered through genetic engineering to contain added or deleted gene sequences. They may contain genes from other organisms to produce a desired trait. Genetic engineering allows for more precise and rapid alteration of organisms compared to traditional breeding methods. Common genetically modified foods include vegetables, tomatoes, potatoes, rice, cheese, and meat. While GM foods could help address world hunger and develop more resilient crops, there are also risks like insects developing pesticide resistance or cross-pollination creating "superweeds". Government agencies regulate GM foods to ensure safety.