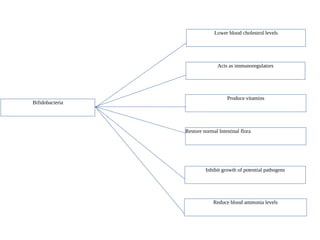
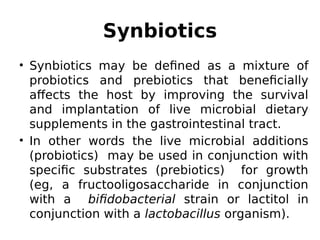
This document discusses probiotics, prebiotics, and synbiotics. It defines probiotics as live microorganisms that provide health benefits when consumed, and defines prebiotics as non-digestible foods that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. Probiotics must adhere to cells, exclude pathogens, persist and multiply in the gut. Prebiotics include oligosaccharides and fibers that feed beneficial bacteria like Bifidobacterium. Synbiotics combine probiotics and prebiotics to improve survival and growth of probiotic bacteria in the gut. Studies show synbiotics can help recovery after surgery by improving the intestinal flora.