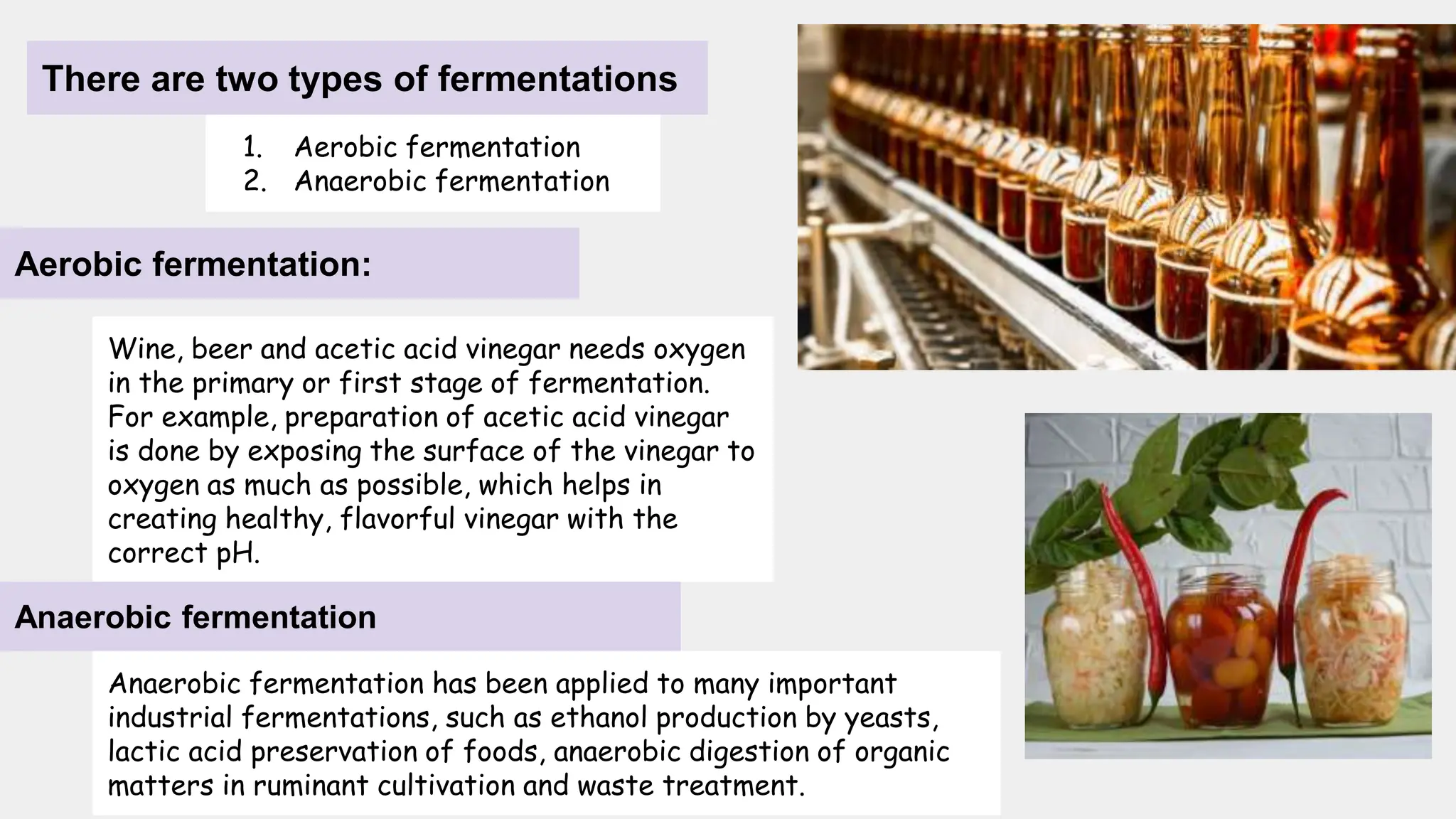
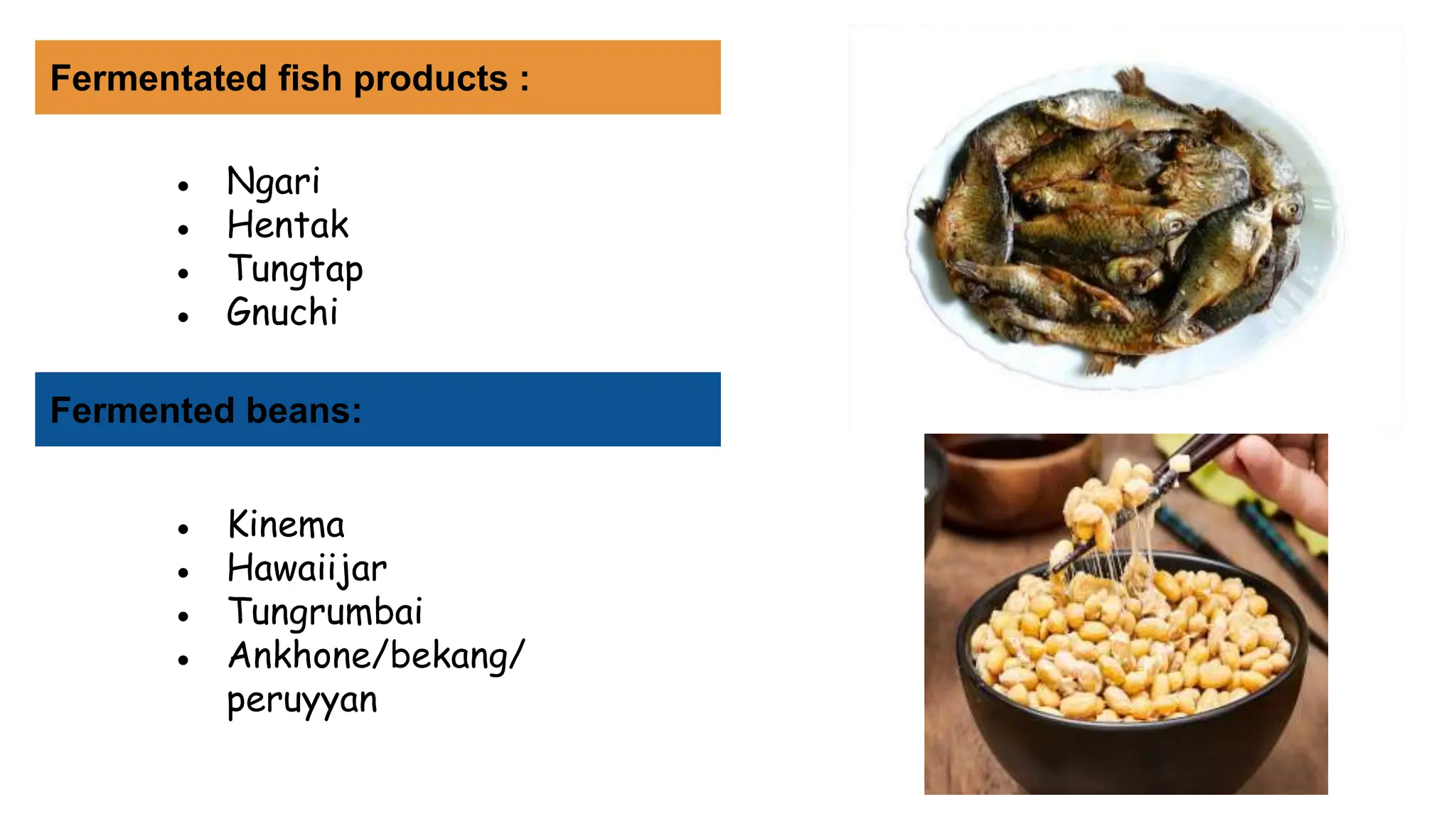
This document discusses food fermentation, which is the conversion of carbohydrates into alcohol or organic acids using microorganisms like yeasts or bacteria under anaerobic conditions. There are two types of fermentation: aerobic and anaerobic. It provides examples of famous fermented foods from around the world and traditional Indian fermented foods. The document also discusses the health benefits of fermented foods as well as potential disadvantages like temporary bloating or headaches in some people.