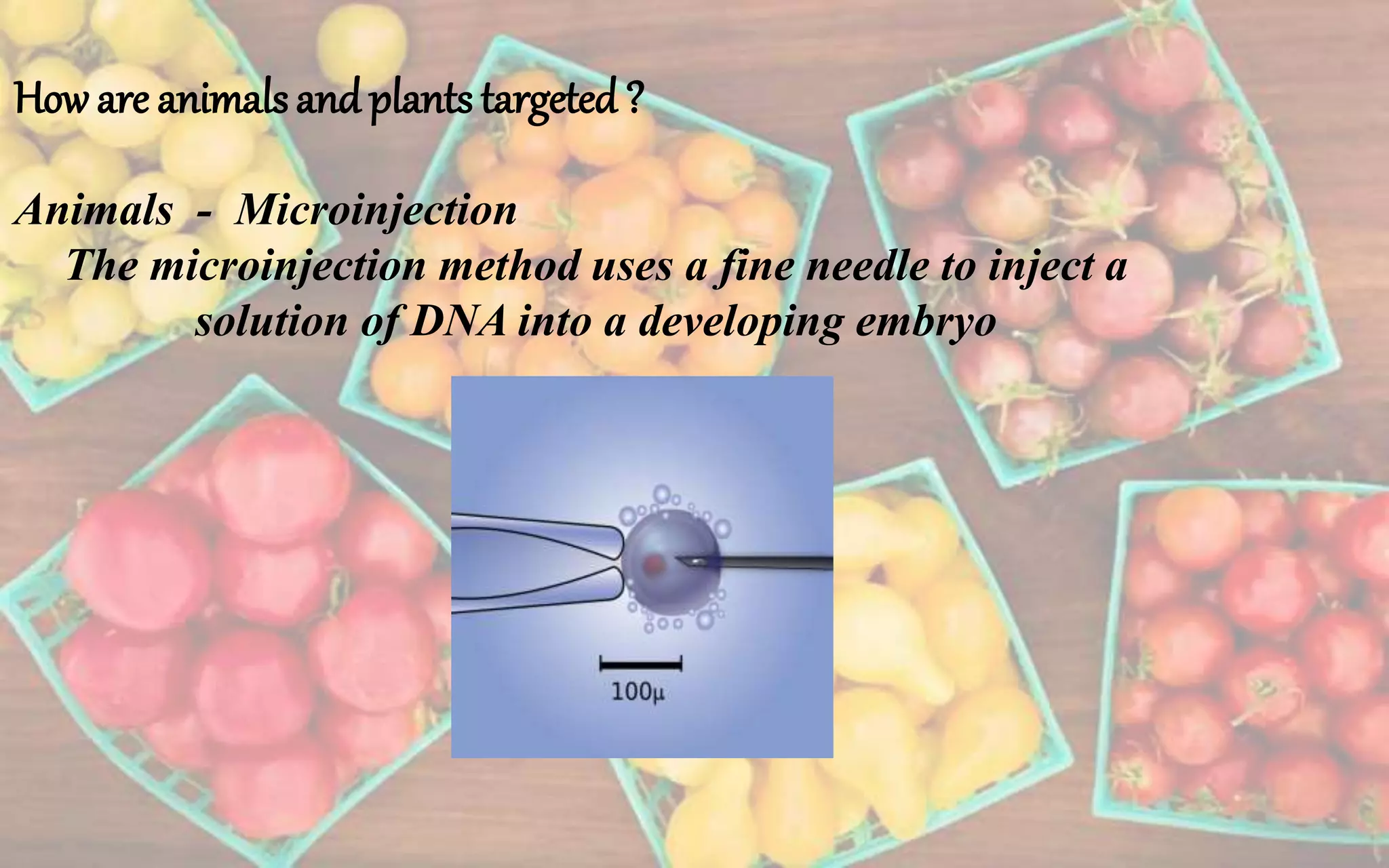
Genetically modified foods are derived from organisms that have had their DNA artificially altered to produce desired characteristics. Recombinant DNA technology is used to transfer genes between organisms, such as adding fish genes to tomatoes to allow them to survive frost. Potential benefits include increased crop yields, reduced pesticide use, and improved nutrition. However, there are also risks like unintended harm to human health from new allergens or to the environment. Government agencies regulate GM foods for safety but labeling is only required in some countries. Overall, GM foods could help address hunger but require cautious assessment of risks.