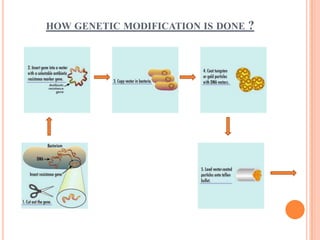
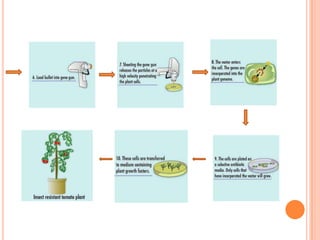
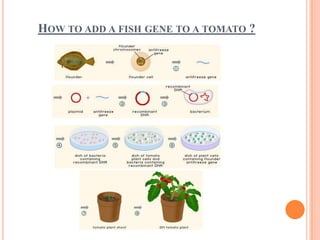
This document discusses genetically modified (GM) foods. GM foods are derived from organisms whose DNA has been altered in a way that does not occur naturally, often by transferring genes between unrelated species. Common GM crops include corn, canola, soybeans, and cotton. Potential benefits include improved yields and nutritional content, while risks involve possible health effects and environmental impacts if GM crops spread unchecked. The conclusion acknowledges GM foods could help address hunger but governments must regulate safely to avoid unintended harm.