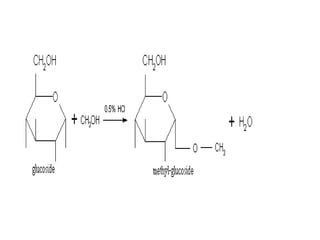
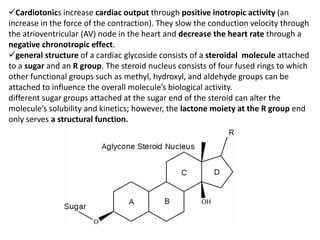
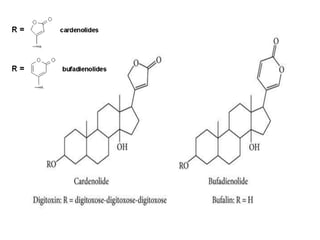
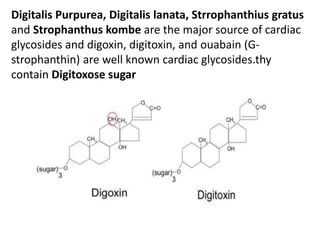
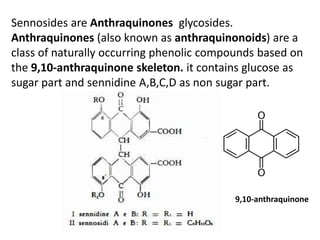
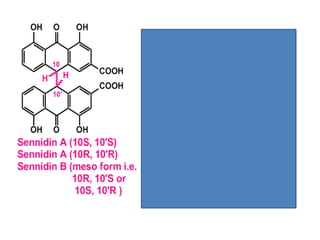
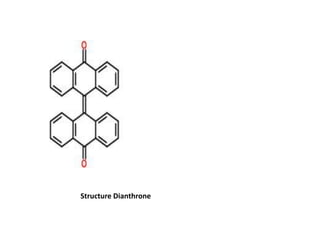
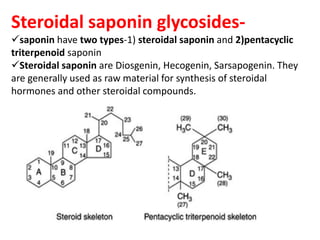
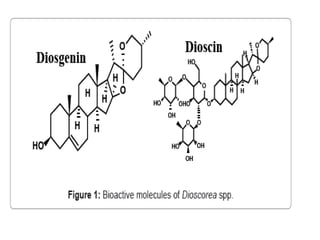
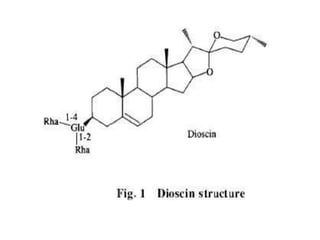
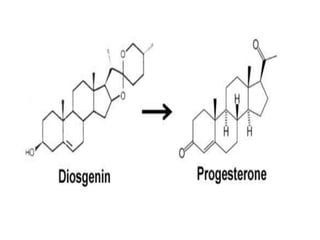
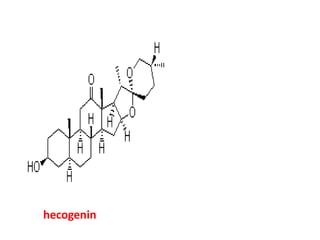
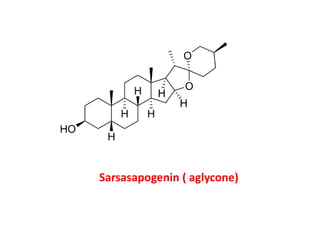
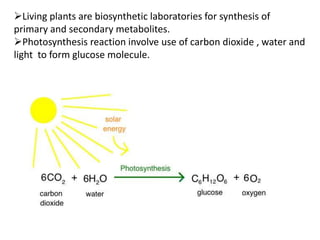
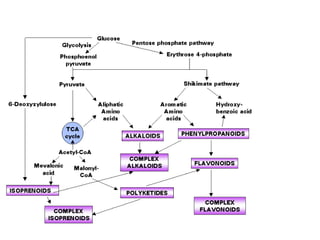
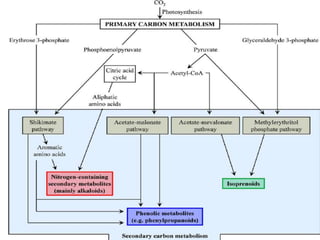
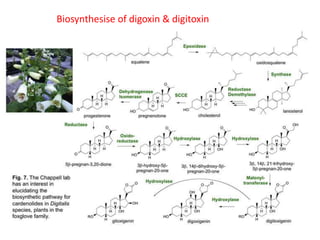
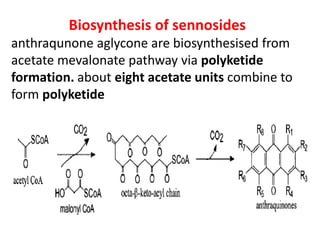
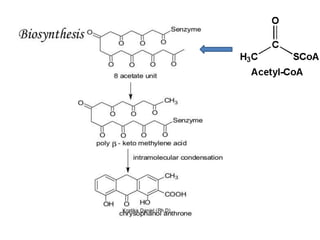
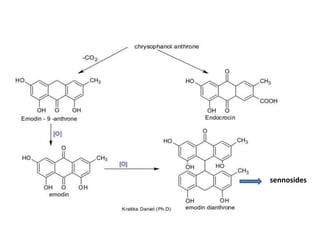
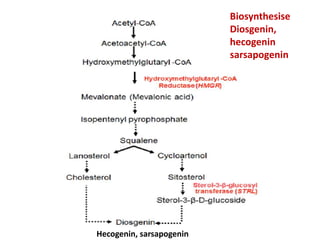
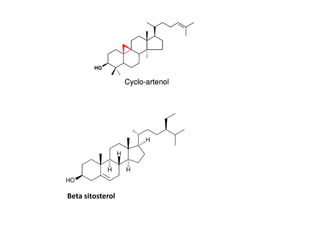
The document discusses the chemistry and biosynthesis of various glycosides. It begins by defining glycosides as molecules composed of a sugar molecule (glycone) linked to a non-sugar molecule (aglycone). It then discusses the chemistry and sources of several classes of glycosides - cardiac glycosides, sennosides, steroidal saponin glycosides like diosgenin, hecogenin and sarsapogenin. The biosynthesis of these glycosides involves the transfer of a sugar molecule from a UDP-sugar to the aglycone, catalyzed by glycosyltransferases. Key cardiac glycosides discussed are digoxin and digitoxin. Sennosides are anthraquinone glycos