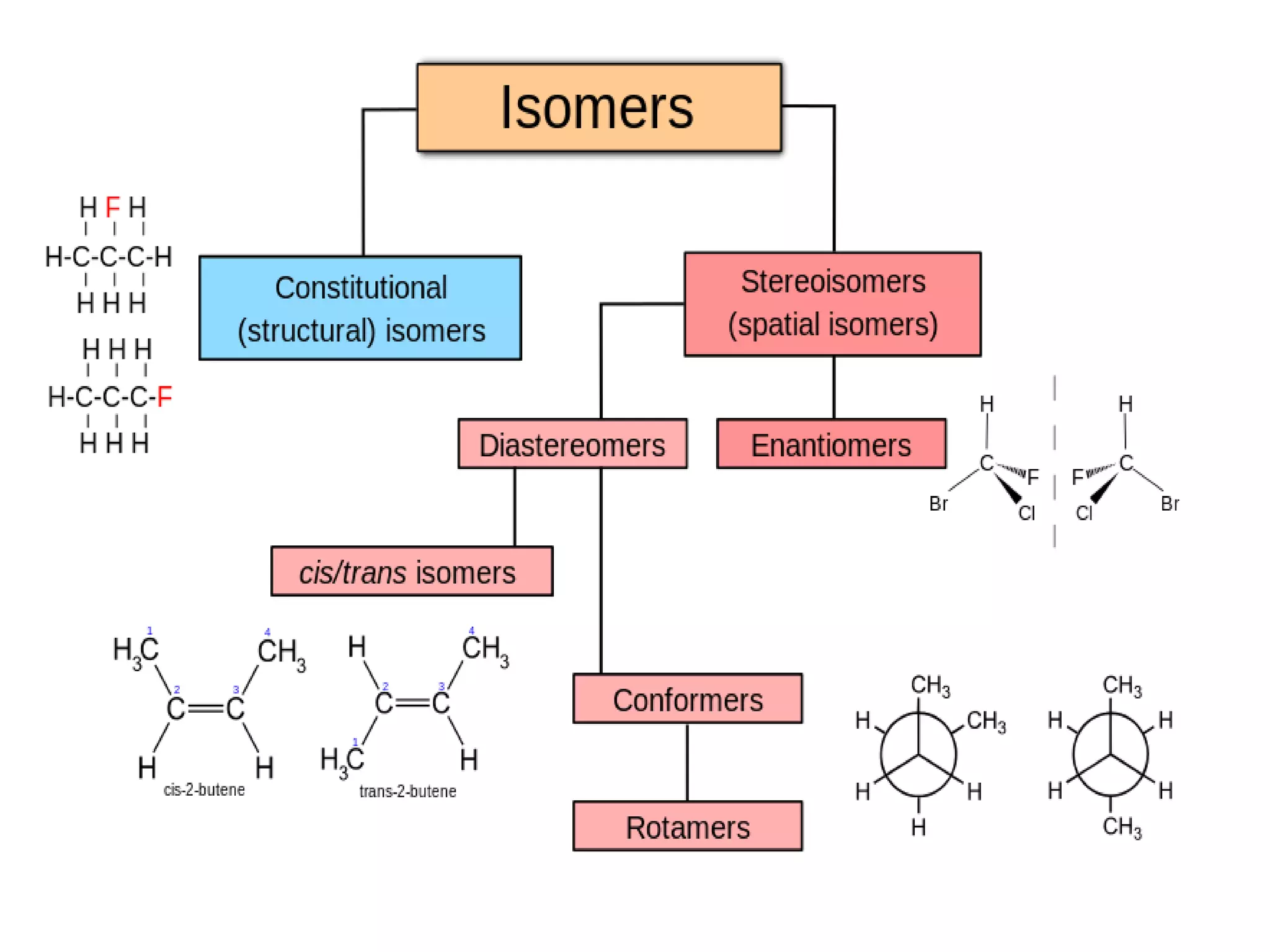
This document discusses different types of isomerism that can occur in natural products, specifically structural isomerism and stereoisomerism. It defines structural isomers as compounds with the same molecular formula but different connectivity of atoms, while stereoisomers have the same atomic structure but different three-dimensional orientations of atoms. There are several types of stereoisomers including enantiomers, which are non-superimposable mirror images, and diastereomers, which are not mirror images. The document provides examples of isomerism in propanol and in alkene double bond geometry.