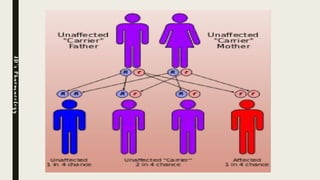
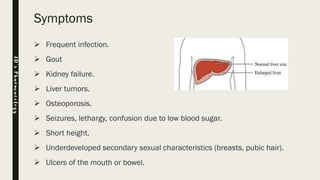
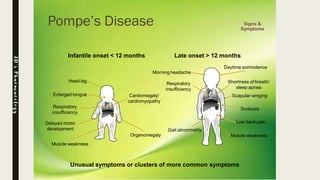
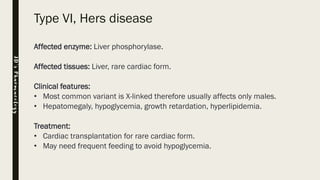
Glycogen storage diseases (GSDs) are inherited metabolic disorders caused by enzyme deficiencies affecting glycogen synthesis and breakdown, primarily in the liver and muscle. There are nine main types of GSDs, including von Gierke's and Pompe's diseases, each with distinct clinical features, symptoms, and treatments. Diagnosis involves blood tests, imaging, and biopsy, while management may include enzyme replacement therapy, dietary changes, and genetic counseling.














![Type XI, Fanconi-Bickel syndrome
Affected enzyme: Glucose transporter GLUT2 [solute carrier family 2, facilitated
glucose transporter]
Clinical features: Similar features to Von Gierke's disease, e.g. hypoglycemia.
JD’sPharmacology](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/jdglycogenstoragedisease-200708145555/85/Glycogen-Storage-Disease-19-320.jpg)




