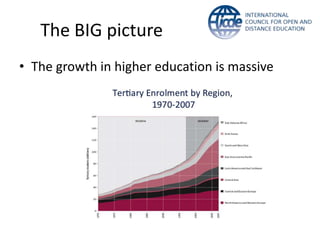
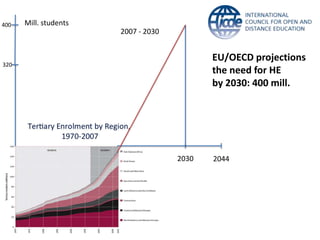
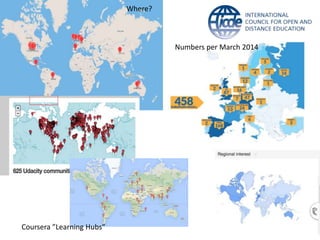
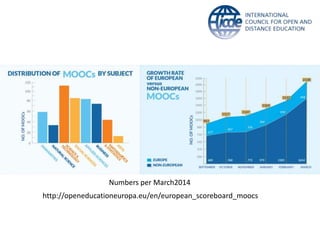
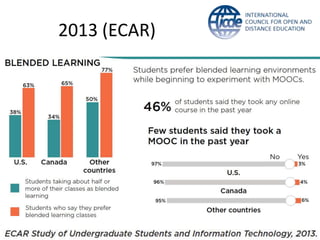
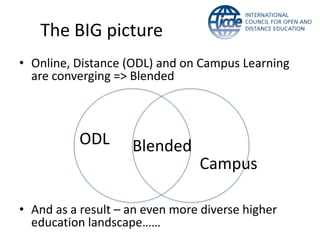
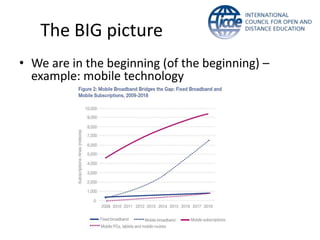
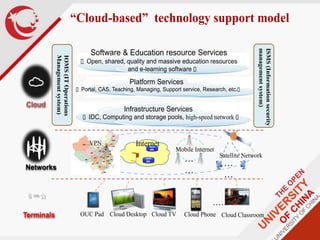
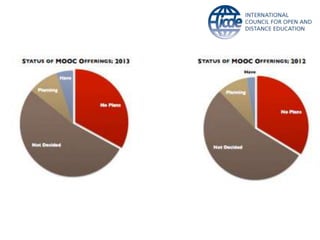
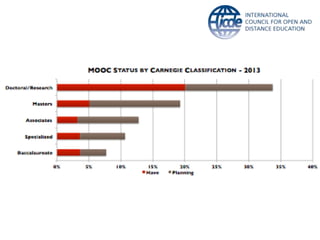
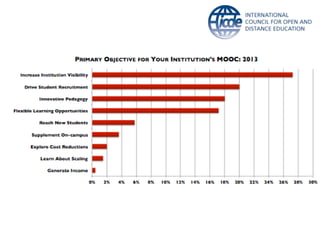
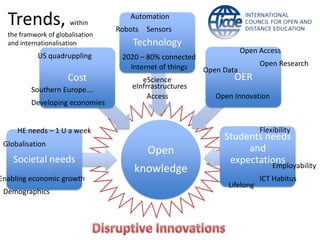
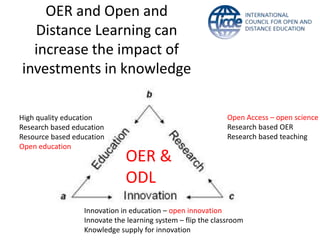
Global online learning is steadily increasing worldwide. MOOCs initially took the world by storm but have since opened up opportunities for massive innovation in education. While MOOCs are initially open in terms of free enrollment, most course content is not openly licensed. Governments are implementing strategies to promote digital learning and the application of information technologies. Online and campus-based learning are converging into blended models. Technological advances will continue to remove barriers to access while new understandings of learning and the brain will shape new pedagogical approaches. We are still in the early stages of these developments.