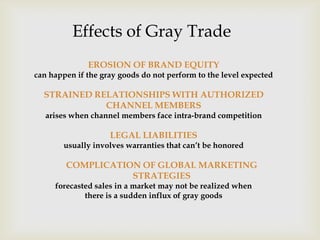
A Global Distribution System (GDS) allows automated transactions between travel vendors and booking agents to provide travel services to consumers. It consolidates distribution globally to allow for low-cost transportation from manufacturing plants and warehouses worldwide to local markets. Elements of international logistics are more complicated than domestic logistics due to more intermediaries, risks, regulations, and challenges of crossing borders. Air, ocean, and overland transportation are used to ship goods internationally considering factors like cost, time, and product characteristics. Gray trade, or parallel distribution of genuine goods through unauthorized channels, can erode brand equity and strain relationships with authorized distributors.