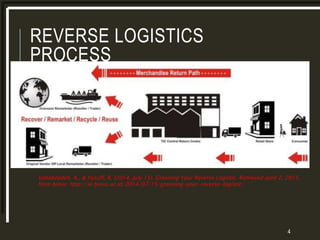
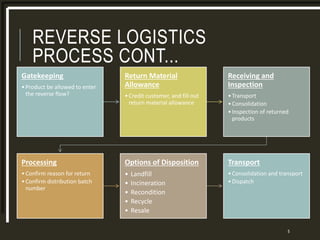
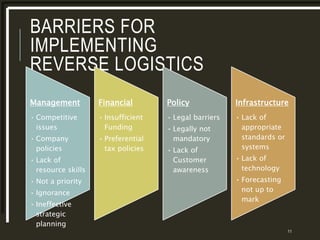
The document provides a comparative analysis of the reverse logistics processes of Woolworths and Coles supermarkets in Australia. It outlines their reverse logistics processes which include collection and disposal of waste, returning goods to suppliers or warehouses, and backhauling to minimize transportation costs and environmental impact. Both companies work with partners for crate and pallet management. Woolworths and Coles also have sustainability strategies focused on reducing waste, emissions, and water usage. They donate surplus food to food banks and implement best practices like efficient stock management and recycling programs.