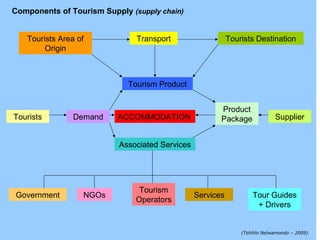
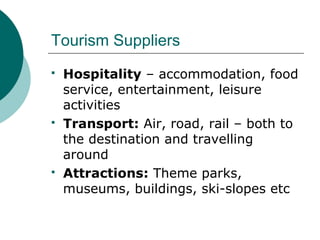
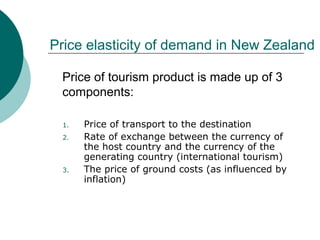
The document discusses supply and demand in tourism. It defines demand and supply, and describes the relationships between price, quantity demanded, and quantity supplied. The four basic laws of supply and demand are outlined. Equilibrium price is defined as the price where supply equals demand. Tourism demand is shaped by factors like income, prices of related goods, and marketing. Tourism supply relies on resources, infrastructure, and services. Supply and demand interactions help determine tourism patterns.


















![Income Elasticity
An individuals income increases their
demand for specific products but reduce
their demand for products previously
consumed.
This is because the change in income may
allow a person to buy a higher-quality
product instead of an inferior product. [Law
of Substitution]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pp8supplyanddemandintourismv1-130919001528-phpapp02/85/Supply-and-demand-in-tourism-20-320.jpg)








![Law of Supply
As the price of a product rises, all
other things being equal , suppliers
will offer more for sale. [As they will
have more to sell since price
increases can dampen demand]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pp8supplyanddemandintourismv1-130919001528-phpapp02/85/Supply-and-demand-in-tourism-29-320.jpg)
![Definition of tourism supply
The supply of all assets, services and goods
to be enjoyed or bought by visitors and
occasioned by the journeys of visitors.
Tourism supply consists of an amalgamation
or mix of attractions. Tourism supply shapes
the demand for tourism in a country.
[Cooper et al – 1993]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pp8supplyanddemandintourismv1-130919001528-phpapp02/85/Supply-and-demand-in-tourism-30-320.jpg)