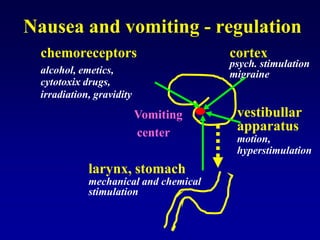
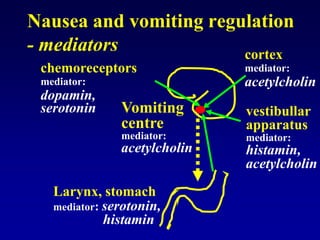
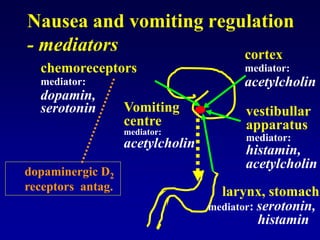
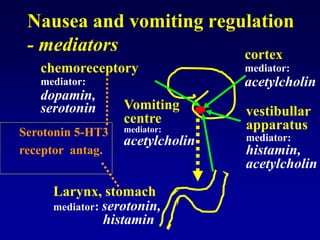
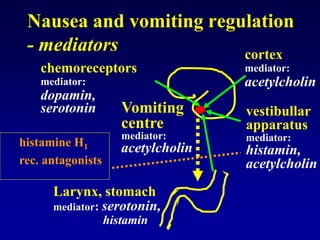
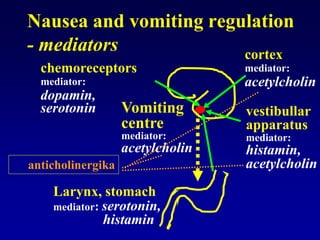
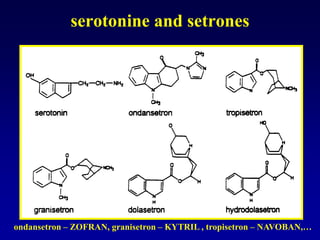
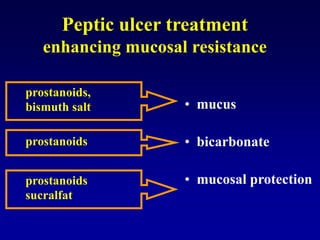
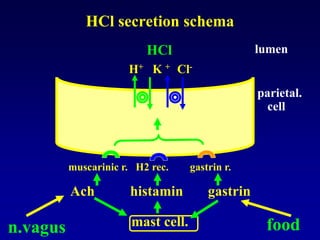
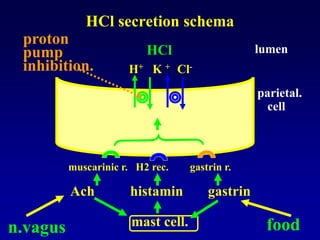
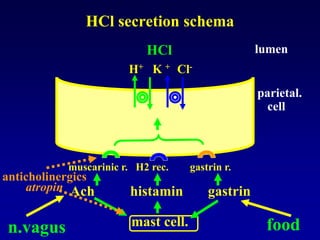
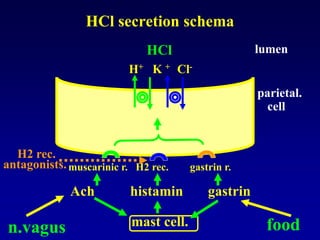
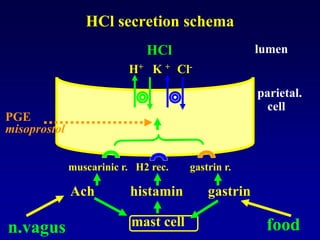
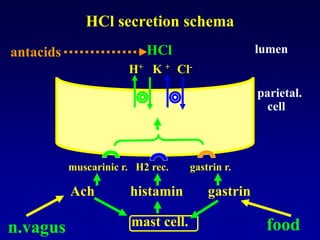
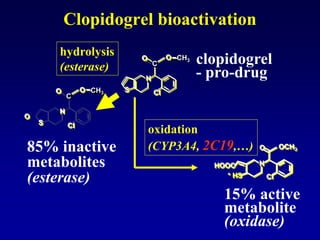
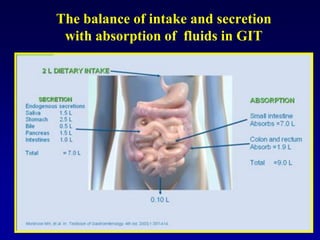
This document discusses the pharmacology of the gastrointestinal tract. It begins by outlining conditions where gastrointestinal intervention may be necessary, such as motility disorders, absorption disorders, and peptic lesions. It then focuses on the regulation of nausea and vomiting, including the vomiting center in the brain and various mediators like dopamine, serotonin, and histamine. It describes different classes of antiemetics that act on these mediators, including serotonin 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, histamine H1 receptor antagonists, and dopamine D2 receptor antagonists. Finally, it discusses prokinetics, treatments for peptic ulcer like proton pump inhibitors, and Helicobacter pylori infection.